912387
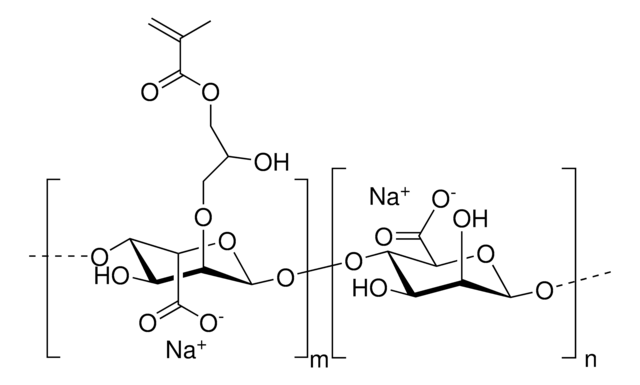
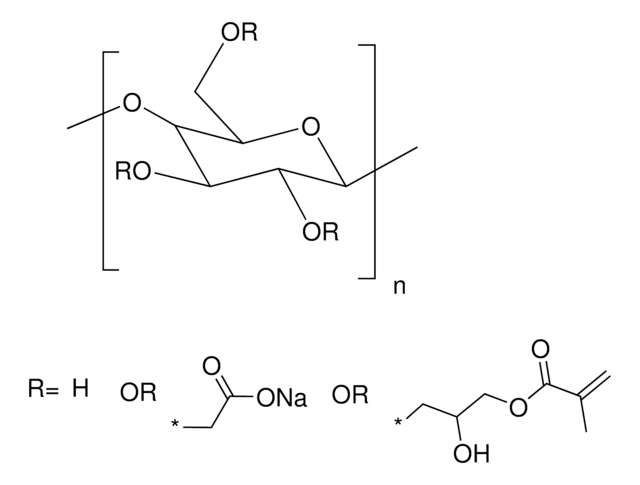
Alginate methacrylate
high viscosity, degree of methacrylation: 20-40%
Synonym(s):
AlMA, Alginate, AlginateMA, Algini acid, Methacrylate-modified alginate, Sodium alginate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
(C13H17O10Na)m(C6H7O7Na)n
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
description
degree of functionalization: 20-40%
Quality Level
form
(Powder or chunk(s) or fibers)
color
light yellow
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Alginate is an anionic polysaccharide that is widely used in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications due to its non-animal origin, low toxicity, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. Alginate hydrogels are commonly used to fabricate tissue engineering scaffolds, bioinks for 3D bioprinting, and nanocarriers for drug & gene delivery. While alginate is commonly crosslinked into a hydrogel via ionic-crosslinking with divalent cations (e.g., Ca2+), these gels feature limited long-term stability due to exchange reactions and migration of divalent cations from the alginate matrix. To prevent matrix degradation, alginate can be functionalized with reactive groups that can be chemically crosslinked, such as methacrylates. Methacrylate-functionalized alginate can be used to prepare hydrogels by thermal or photochemical crosslinking of the terminal methacrylates. Properties of the resulting hydrogel (e.g., stiffness, swelling ratio, rate of degradation) can be tuned by alginate molecular weight, degree of methacrylate functionalization, and crosslink density.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Photocrosslinkable polysaccharides for in situ hydrogel formation
Smeds K A and Grinstaff M W
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 54 (1), 115-112 (2001)
Siddhesh N Pawar et al.
Biomaterials, 33(11), 3279-3305 (2012-01-28)
Alginates have become an extremely important family of polysaccharides because of their utility in preparing hydrogels at mild pH and temperature conditions, suitable for sensitive biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids, and even for living cells such as islets of
Andrew D Rouillard et al.
Tissue engineering. Part C, Methods, 17(2), 173-179 (2010-08-14)
Methods for seeding high-viability (>85%) three-dimensional (3D) alginate-chondrocyte hydrogel scaffolds are presented that employ photocrosslinking of methacrylate-modified alginate with the photoinitiator VA-086. Comparison with results from several other photoinitiators, including Irgacure 2959, highlights the role of solvent, ultraviolet exposure, and
Oju Jeon et al.
Biomaterials, 30(14), 2724-2734 (2009-02-10)
Photocrosslinked and biodegradable alginate hydrogels were engineered for biomedical applications. Photocrosslinkable alginate macromers were prepared by reacting sodium alginate and 2-aminoethyl methacrylate in the presence of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide. Methacrylated alginates were photocrosslinked using ultraviolet light with 0.05% photoinitiator.
Jia Jia et al.
Acta biomaterialia, 10(10), 4323-4331 (2014-07-08)
Recent advances in three-dimensional (3-D) printing offer an excellent opportunity to address critical challenges faced by current tissue engineering approaches. Alginate hydrogels have been used extensively as bioinks for 3-D bioprinting. However, most previous research has focused on native alginates
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service