906972
F-M
≥98%
Synonym(s):
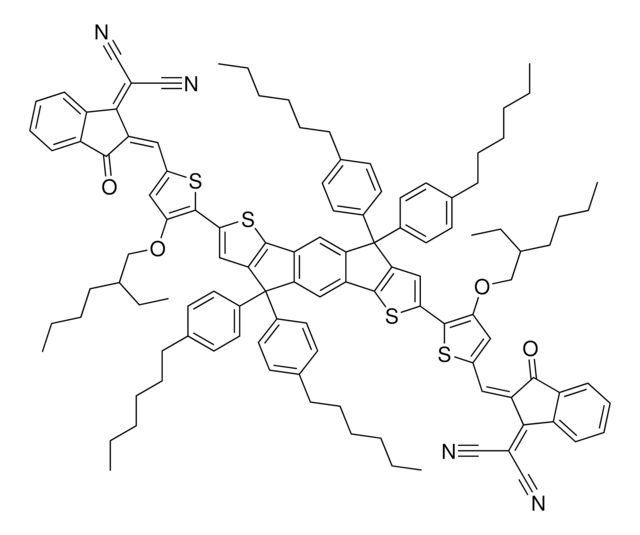
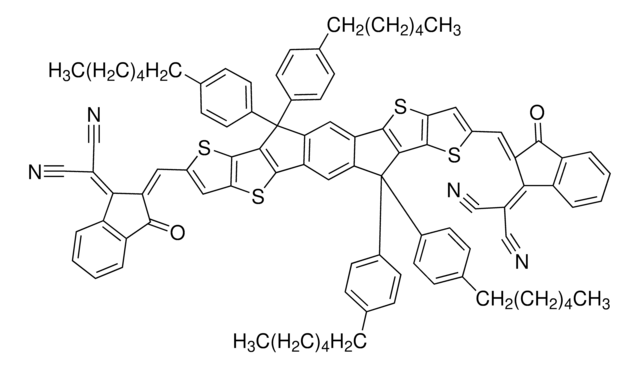
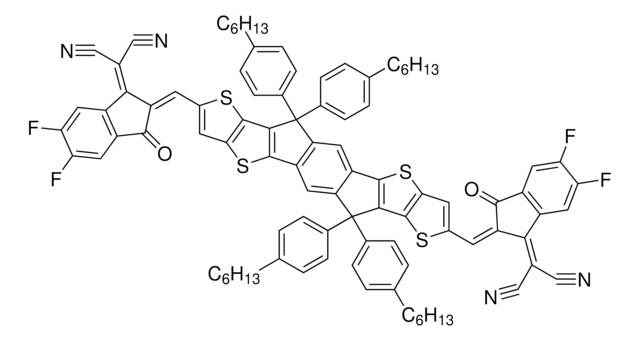
4,4,7,7,12,12-octyl-7,12-dihydro- bis[methylidyne(3-oxo-methyl-1H indene-2,1(3H)-diylidene)]]bis-4H-thieno[2″,3″:1′,2′]indeno[5′,6′:5,6]-s-indaceno[1,2-b]thiophene, FTIC-C8C8M
About This Item
Recommended Products
description
Band gap: 1.72 eV
Band gap: Eg = 1.72 eV
Solubility: Soluble in Chloroform, CB and ODCB
Assay
≥98%
form
solid
Orbital energy
HOMO -5.42 eV
LUMO -3.70 eV
SMILES string
[s]1c2c(cc1\C=C%10/C(=O)c%11c(cccc%11)C/%10=C(C#N)C#N)C(c3c2cc4c(c3)c5c(cc6c(c5)C(c7c6[s]c(c7)\C=C8/C(=O)c9c(cccc9)C/8=C(C#N)C#N)(CCCCCCCC)CCCCCCCC)C4(CCCCCCCC)CCCCCCCC)(CCCCCCCC)CCCCCCCC.CC.CC
InChI key
XPHYXDLZYTYOBX-OMQJLYAYSA-N
General description
Application
Tandem Cell Device performance:
ITO/ZnO/PFN-Br/PBDB-T:F-M/M-PEDOT/ZnO/PTB7- Th:O6T-4F:PC71BM/MoO3/Ag
Voc=1.642 V
Jsc=14.35 mA/cm2
FF=73.7%
PCE=17.3%
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The emerging organic photovoltaic (OPV) technology is very promising for low-cost solar energy production. OPV devices can be produced using high-throughput, large-volume printing methods on lightweight and flexible plastic substrates, making them easy to deploy and use in innovative ways.
Professor Chen (Nankai University, China) and his team explain the strategies behind their recent record-breaking organic solar cells, reaching a power conversion efficiency of 17.3%.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service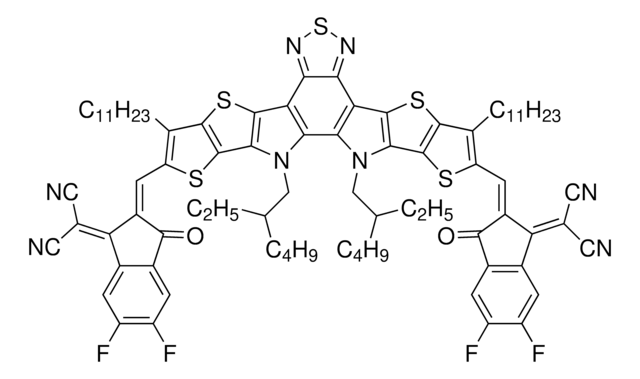


![[6,6]-Phenyl C71 butyric acid methyl ester, mixture of isomers 99%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/716/624/9fb9f2f0-ae99-429f-8d3a-b12267976a4d/640/9fb9f2f0-ae99-429f-8d3a-b12267976a4d.png)