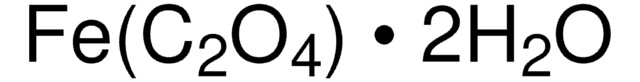436011
Iron(III) phosphate dihydrate
Fe 29 %
Synonym(s):
Ferric phosphate dihydrate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
FePO4 · 2H2O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
186.85
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12161600
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
form
powder
Quality Level
composition
Fe, 29%
reaction suitability
core: iron
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Cross Couplings
functional group
amine
phosphine
SMILES string
O.O.[Fe+3].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O
InChI
1S/Fe.H3O4P.2H2O/c;1-5(2,3)4;;/h;(H3,1,2,3,4);2*1H2/q+3;;;/p-3
InChI key
BMTOKWDUYJKSCN-UHFFFAOYSA-K
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
Iron(III) phosphate dihydrate (FePO4 x 2H2O) can be used as a catalyst in the synthesis of:
It can be also used in the synthesis of carbon coated lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) as the cathode material for lithium ion batteries. It is also used as a key ingredient in preparing phosphate glass fibers.
- 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones and thiones by reacting with aldehydes, β-ketoesters and urea/thiourea via one pot-three component Biginelli reaction.
- Methyl methacryalate (MMA) by oxidative dehydrogenation of methyl iso-butarate (MIB).
It can be also used in the synthesis of carbon coated lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) as the cathode material for lithium ion batteries. It is also used as a key ingredient in preparing phosphate glass fibers.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Structural and electrochemical study of a new crystalline hydrated iron (III) phosphate FePO4
Marx N, et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 22(5), 1854-1861 (2010)
An Oxidative Route for the Production of Methyl Methacrylate: A Study Over Iron Phosphate Catalysts
Harilal A, et al.
Catalysis Letters, 146(7), 1169-1181 (2016)
A novel process to recycle spent LiFePO4 for synthesizing LiFePO4/C hierarchical microflowers
Bian D, et al.
Electrochimica Acta, 190(5), 134-140 (2016)
Fabian Rohner et al.
The Journal of nutrition, 137(3), 614-619 (2007-02-22)
Particle size is a determinant of iron (Fe) absorption from poorly soluble Fe compounds. Decreasing the particle size of metallic Fe and ferric pyrophosphate added to foods increases Fe absorption. The aim of this study was to develop and characterize
Tao Zhang et al.
Journal of hazardous materials, 176(1-3), 444-450 (2009-12-17)
Phosphorus removal and recovery by ferric phosphate (FePO(4) x 2 H(2)O) precipitation has been considered as an effective technology. In the present study, we examined chemical precipitation thermodynamic modeling of the PHREEQC program for phosphorus removal and recovery from wastewater.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service