C4063
C Reactive Protein from human fluids
buffered aqueous solution
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human fluids
Quality Level
Assay
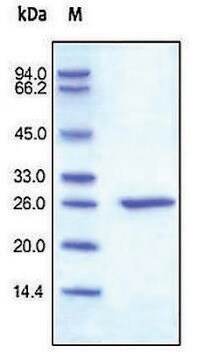
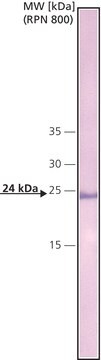
≥90% (SDS-GE)
form
buffered aqueous solution
UniProt accession no.
application(s)
cell analysis
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
human ... CRP(1401)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
C Reactive Protein (CRP) is a homopentameric protein, which belongs to the pentraxin family. It is produced in liver hepatocytes, smooth muscle cells, macrophages and adipocytes. CRP gene is located on human chromosome 1q23.2.
Application
C Reactive Protein from human fluids has been used:
- to investigate the neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)-dependent generation of monomeric CRP (mCRP) from pentameric CRP (pCRP)
- to evaluate its effects on areas at risk (AAR) of myocardium with ischemia-reperfusion injury
- to measure intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Biochem/physiol Actions
C Reactive Protein (CRP) plays a critical role in apoptosis, phagocytosis, nitric oxide (NO) release and the secretion of cytokines, such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α. CRP acts as a marker for cardiovascular diseases, rheumatoid arthritis and cancer.
C reactive protein (CRP) is an acute phase protein. Serum levels in patients with atherosclerosis is predictive of increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke. The cytokine IL-6 is thought to be the key mediator in hepatocyte secretion of acute phase proteins including CRP. CRP mediates innate immunity by binding to microbial polysaccharides and to ligands exposed on damaged cells. The binding activates the classical complement pathway (C1, C4, C2, C3 but not C5-9). Opsonization of the substrates leads to their uptake by phagocytic cells and limits the inflammatory response.
C reactive protein (CRP) is an acute phase protein. Serum levels in patients with atherosclerosis is predictive of increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke. The cytokine IL-6 is thought to be the key mediator in hepatocyte secretion of acute phase proteins including CRP. CRP mediates innate immunity by binding to microbial polysaccharides and to ligands exposed on damaged cells. The binding activates the classical complement pathway (C1, C4, C2, C3 but not C5-9). Opsonization of the substrates leads to their uptake by phagocytic cells and limits the inflammatory response.
Packaging
Package size based on protein content.
Other Notes
CRP is isolated from human fluids (Ascitic/Pleural).
Physical form
Solution in 0.02 M Tris, 0.28 M sodium chloride, 0.005 M calcium chloride, pH 7.8 - 8.2, containing 0.1% sodium azide.
Analysis Note
Protein determined by Lowry.
Disclaimer
RESEARCH USE ONLY. This product is regulated in France when intended to be used for scientific purposes, including for import and export activities (Article L 1211-1 paragraph 2 of the Public Health Code). The purchaser (i.e. enduser) is required to obtain an import authorization from the France Ministry of Research referred in the Article L1245-5-1 II. of Public Health Code. By ordering this product, you are confirming that you have obtained the proper import authorization.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Eun Na Kim et al.
PloS one, 14(5), e0216610-e0216610 (2019-05-08)
Prognosis of myocardial infarction tends to be worse when serum C-reactive protein (CRP) level is high. miRNAs are also known to be involved in different pathogeneses of heart diseases such as myocardial infarction. However, how CRP is involved in myocardial
Yoshiko Fujita et al.
Clinical chemistry, 55(2), 285-294 (2008-12-17)
C-reactive protein (CRP) exerts biological activity on vascular endothelial cells. This activity may promote atherothrombosis, but the effects of this activity are still controversial. Lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1), the oxidized LDL receptor on endothelial cells, is involved in endothelial
Sofia Ramiro et al.
Annals of the rheumatic diseases, 73(8), 1455-1461 (2014-05-09)
To analyse the long-term relationship between disease activity and radiographic damage in the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Patients from the Outcome in AS International Study (OASIS) were followed up for 12 years, with 2-yearly clinical and radiographic assessments.
Alice S Ryan et al.
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 62(4), 607-614 (2014-03-19)
To examine the relationships between plasma and tissue markers of systemic and vascular inflammation and obesity and insulin resistance and determine the effects of aerobic exercise training plus weight loss (AEX+WL) and weight loss (WL) alone on these biomarkers. Prospective
C-reactive protein promotes atherosclerosis by increasing LDL transcytosis across endothelial cells
Bian F, et al.
British Journal of Pharmacology, 171(10), 2671-2684 (2014)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service