520268
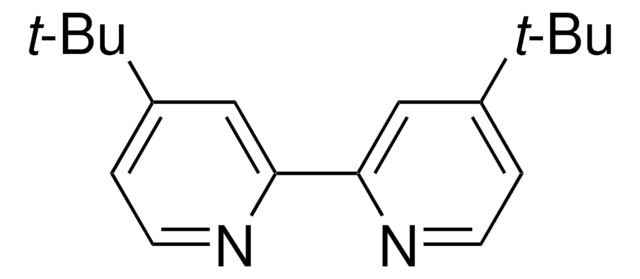
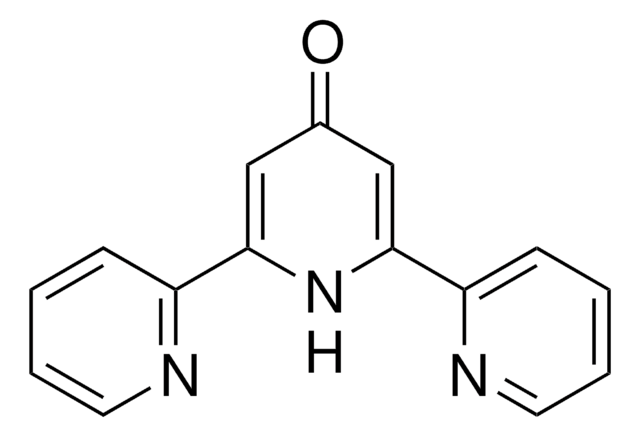
4,4′,4″-Tri-tert-Butyl-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine
95%
Synonym(s):
2,6-Bis[4-(tert-butyl)pyridin-2-yl)-4-(tert-butyl)pyridine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C27H35N3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
401.59
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Assay
95%
impurities
oligomers of tert-butyl-terpyridine
mp
215-217 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CC(C)(C)c1ccnc(c1)-c2cc(cc(n2)-c3cc(ccn3)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)C
InChI
1S/C27H35N3/c1-25(2,3)18-10-12-28-21(14-18)23-16-20(27(7,8)9)17-24(30-23)22-15-19(11-13-29-22)26(4,5)6/h10-17H,1-9H3
InChI key
QMABMHJGSFUTPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
4,4′,4″-Tri-tert-Butyl-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine is a terpyridine (terpy) ligands that is commonly used in organic synthesis due to its role in coordination chemistry, particularly in the formation of metal complexes such as Zn(II), Cd, and lanthanide-cadmium pentafluorobenzoate complexes.
Application
4,4′,4-Tri-tert-Butyl-2,2′:6′,2-terpyridine can be used as a ligand:
- In the synthesis of methylated alkanes and ketones via Ni-catalyzed methylation of unactivated alkyl halides and acid chlorides.
- In Ni-catalyzed reductive dimerization reaction.
- In allylic defluorinative reductive cross-coupling reaction in the presence of Ni as a catalyst.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Zhuye Liang et al.
Organic letters, 16(21), 5620-5623 (2014-10-22)
Methylation of unactivated alkyl halides and acid chlorides under Ni-catalyzed reductive coupling conditions led to efficient formation of methylated alkanes and ketones using methyl p-methyl tosylate as the methylation reagent. Moderate to excellent coupling yields as well as excellent functional
Xiao-Yu Lu et al.
Organic & biomolecular chemistry, 18(19), 3674-3678 (2020-05-08)
A nickel-catalyzed defluorinative reductive cross-coupling of trifluoromethyl alkenes with epoxides has been developed. Various substituted trifluoromethyl alkenes and epoxides were found to be suitable reaction substrates. This reaction enabled C(sp3)-C(sp3) bond construction through allylic defluorinative cross-coupling of trifluoromethyl alkenes under
Michael R Prinsell et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 46(31), 5743-5745 (2010-06-29)
The first general method for the reductive dimerization of alkyl halides, alkyl mesylates, alkyl trifluoroacetates, and allylic acetates is reported which proceeds with low catalyst loading (0.5 to 5 mol%), generally high yields (80% ave yield), and good functional-group tolerance.
Cheng-Pan Zhang et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 135(22), 8141-8144 (2013-05-23)
Mechanistic proposals for nickel-catalyzed coupling reactions often invoke five-coordinate alkyl- or aryl-bound Ni(II) and/or high-valent nickel(III) species, but because of their reactive nature, they have been difficult to study and fingerprint. In this work, we invoked the stabilizing properties of
Gavin D Jones et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 128(40), 13175-13183 (2006-10-05)
The ability of the terpyridine ligand to stabilize alkyl complexes of nickel has been central in obtaining a fundamental understanding of the key processes involved in alkyl-alkyl cross-coupling reactions. Here, mechanistic studies using isotopically labeled (TMEDA)NiMe(2) (TMEDA = N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine) have
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service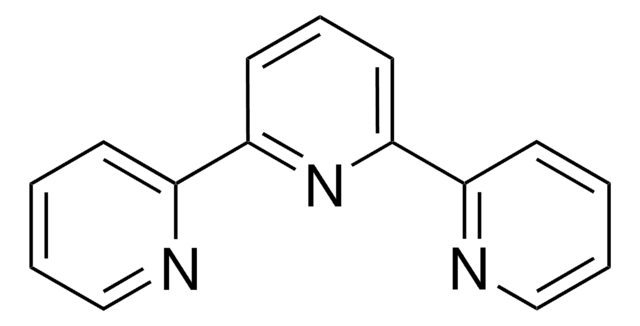


![2,6-Bis[(4R)-(+)-isopropyl-2-oxazolin-2-yl]pyridine 99%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/349/609/8673c46e-368a-47a6-a9bd-52bbe13d490a/640/8673c46e-368a-47a6-a9bd-52bbe13d490a.png)