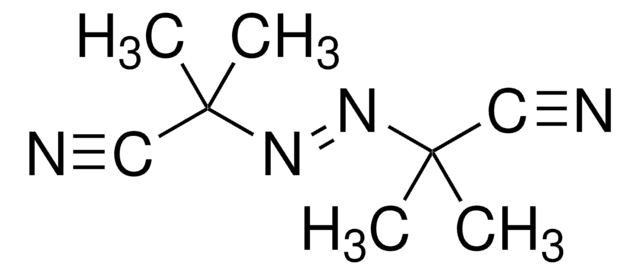
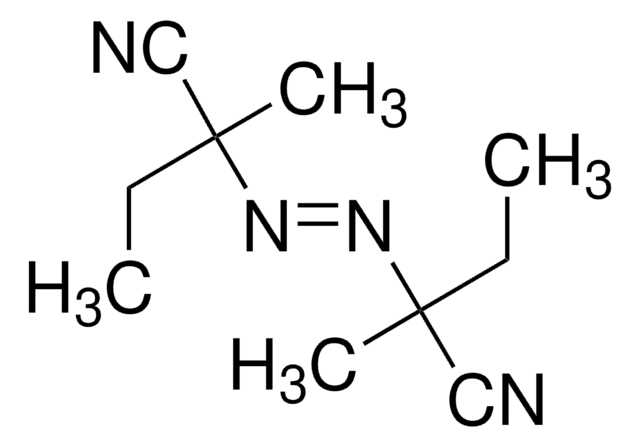
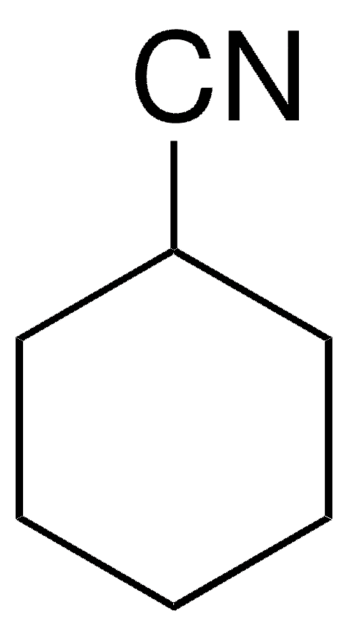
380210
1,1′-Azobis(cyclohexanecarbonitrile)
98%
Synonym(s):
1,1′-Azobis(cyanocyclohexane), ACHN
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
form
solid
mp
114-118 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
N#CC1(CCCCC1)\N=N\C2(CCCCC2)C#N
InChI
1S/C14H20N4/c15-11-13(7-3-1-4-8-13)17-18-14(12-16)9-5-2-6-10-14/h1-10H2/b18-17+
InChI key
KYIKRXIYLAGAKQ-ISLYRVAYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Self-react. D - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
5.2 - Organic peroxides and self-reacting hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
We presents an article about Copper(I)-mediated Living Radical Polymerization in the Presence of Pyridylmethanimine Ligands, and the emergence of living radical polymerization mediated by transition metal catalysts in 1995, which was a seminal piece of work in the field of synthetic polymer chemistry.
Applying ARGET ATRP to the Growth of Polymer Brush Thin Films by Surface-initiated Polymerization
Protocols
We present an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
An article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service