T8552
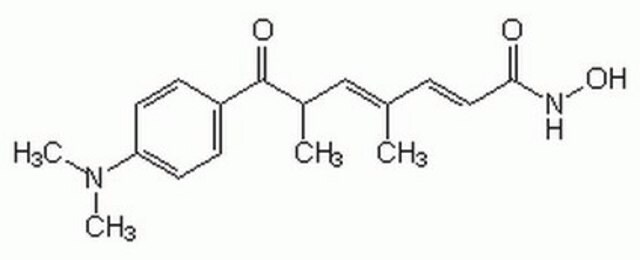
Trichostatin A
≥98% (HPLC), from Streptomyces sp.
Synonym(e):
TSA, [R-(E,E)]-7-[4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl]-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyl-7-oxo-2,4-heptadienamid
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Biologische Quelle
Streptomyces sp.
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
Form
powder
Löslichkeit
methanol: soluble 1.90-2.10 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faint yellow or tan
DMF: soluble
DMSO: soluble
H2O: insoluble
acetone: slightly soluble
acetonitrile: soluble
benzene: slightly soluble
chloroform: slightly soluble
ethanol: soluble
ethyl acetate: slightly soluble
lower alcohols: soluble
Lagertemp.
−20°C
SMILES String
C[C@H](\C=C(C)\C=C\C(=O)NO)C(=O)c1ccc(cc1)N(C)C
InChI
1S/C17H22N2O3/c1-12(5-10-16(20)18-22)11-13(2)17(21)14-6-8-15(9-7-14)19(3)4/h5-11,13,22H,1-4H3,(H,18,20)/b10-5+,12-11+/t13-/m1/s1
InChIKey
RTKIYFITIVXBLE-QEQCGCAPSA-N
Angaben zum Gen
human ... HDAC1(3065) , HDAC4(9759) , HDAC6(10013) , HDAC8(55869)
mouse ... ENSMUSG00000061062(15181)
rat ... Hdac7a(84582)
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
Angaben zur Herstellung
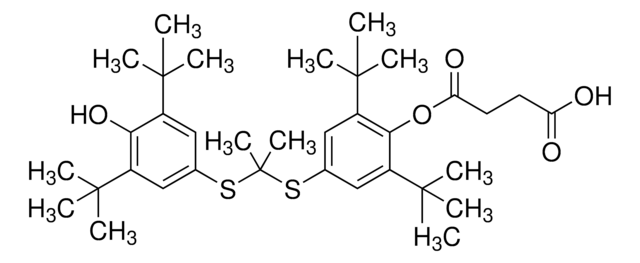
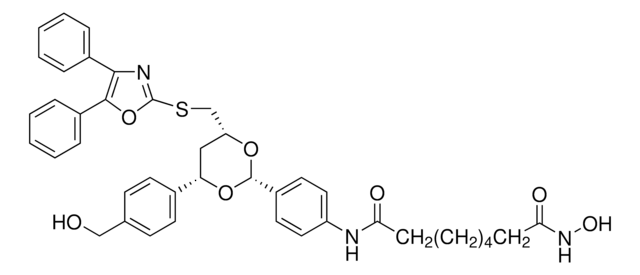
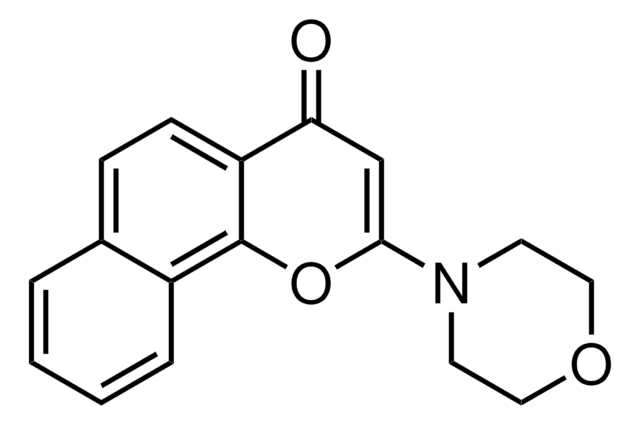
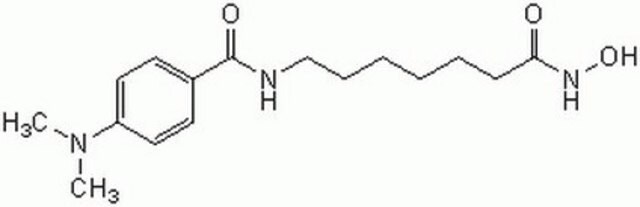
Ähnliches Produkt
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Cancer research has revealed that the classical model of carcinogenesis, a three step process consisting of initiation, promotion, and progression, is not complete.
Epigenetic modifications are thought to occur through two key interconnected processes—DNA methylation and the covalent modification of histones.
Verwandter Inhalt
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death (PCD), is a selective process for the removal of unnecessary, infected or transformed cells in various biological systems. As it plays a role in the homeostasis of multicellular organisms, apoptosis is tightly regulated through two principal pathways by a number of regulatory and effector molecules.
n proliferating cells, the cell cycle consists of four phases. Gap 1 (G1) is the interval between mitosis and DNA replication that is characterized by cell growth. Replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis (S) phase, which is followed by a second gap phase (G2) during which growth and preparation for cell division occurs. Together, these three stages comprise the interphase phase of the cell cycle. Interphase is followed by the mitotic (M) phase.
We offer a variety of small molecule research tools, such as transcription factor modulators, inhibitors of chromatin modifying enzymes, and agonists/antagonists for target identification and validation in gene regulation research; a selection of these research tools is shown below.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.