Wichtige Dokumente
SML2146
SR-18292 Maleate
≥98% (HPLC)
Synonym(e):
SR-18292 Maleate, 1-[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]amino]-3-(1H-indol-4-yloxy)-2-propanol maleate, SR 18292, SR 18292 maleate
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
Form
powder
Farbe
white to beige
Löslichkeit
DMSO: 2 mg/mL, clear
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
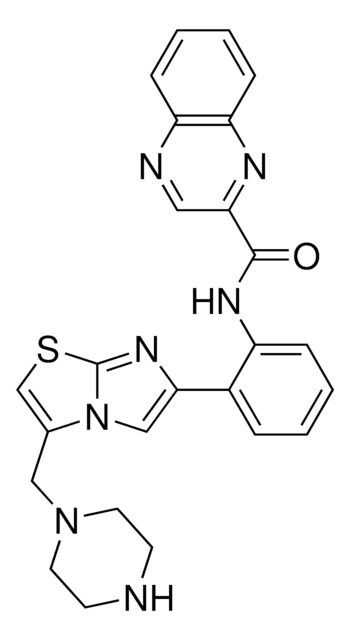
CC(C)(C)N(CC(O)COC1=CC=CC2=C1C=CN2)CC3=CC=C(C)C=C3.O=C(O)/C=C\C(O)=O
InChIKey
CMTOYDGVFTZNSM-BTJKTKAUSA-N
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Dokumente section.
Wenn Sie Hilfe benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an Kundensupport
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.