Wichtige Dokumente
SMB00609
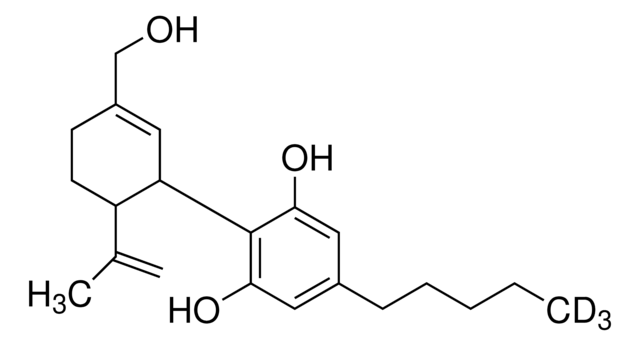
6,6′-Dihydroxythiobinupharidine
≥95% (HPLC)
Synonym(e):
6,6′-Dihydroxythionuphlutine A, Nuphleine
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
Form
powder
Wirkungsspektrum von Antibiotika
Gram-positive bacteria
Wirkungsweise
enzyme | inhibits
Lagertemp.
−20°C
SMILES String
O[C@H]1N2[C@@]([C@H](C)CC[C@H]2C3=COC=C3)([H])CC[C@@]14SC[C@]5(C4)CC[C@]([C@H](C)CC[C@H]6C7=COC=C7)([H])N6[C@@H]5O
InChI
1S/C30H42N2O4S/c1-19-3-5-25(21-9-13-35-15-21)31-23(19)7-11-29(27(31)33)17-30(37-18-29)12-8-24-20(2)4-6-26(32(24)28(30)34)22-10-14-36-16-22/h9-10,13-16,19-20,23-28,33-34H,3-8,11-12,17-18H2,1-2H3/t19-,20-,23+,24+,25+,26+,27-,28-,29-,30+/m1/s1
InChIKey
DYEOLAMWQVWASS-XKCSGWQSSA-N
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
It was also found to act synergistically with cytotoxic drugs such as cisplatin and etoposide, enabling their cytotoxic effect at lower concentrations.
6,6′-Dihydroxythiobinupharidine was found to have cytotoxic activity at a concentration of ~10 μM on human leukemia cells (U937), mouse melanoma cells (B16F10), and human fibroblasts (HT1080).
In addition, Nuphar lutea extract was effective against both Leishmania promastigote and amastigote forms (IC50 = 2 ± 0.12 μg/mL; ID50 = 0.65 ± 0.023 μg/mL; LD50 = 2.1 ± 0.096 μg/mL, STI = 3.23). A synergistic antileishmanial activity was demonstrated with the antileishmanial drug, paromomycin.
Recently 6,6′-dihydroxythiobinupharidine was found to be active against MRSA and VRE strains with an MIC of 1-4 μg/mL. Inhibition of DNA topoisomerase IV but not DNA gyrase in S. aureus was suggested as the mechanism of action. 6,6′-Dihydroxythiobinupharidine was also shown to promote neutrophil effector bactericidal functions.
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Die passende Version wird nicht angezeigt?
Wenn Sie eine bestimmte Version benötigen, können Sie anhand der Lot- oder Chargennummer nach einem spezifischen Zertifikat suchen.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.