Wichtige Dokumente
11189
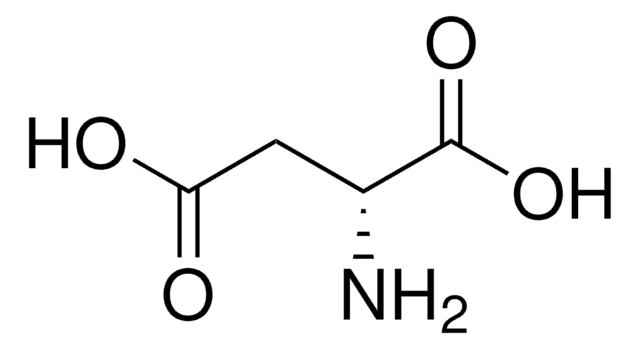
L-Asparaginsäure
≥99.5% (T), BioUltra
Synonym(e):
(S)-2-Amino-bernsteinsäure, (S)-2-Aminobutandisäure
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
product name
L-Asparaginsäure, BioUltra, ≥99.5% (T)
Produktlinie
BioUltra
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥99.5% (T)
Form
powder or crystals
Optische Aktivität
[α]20/D +24.7±1°, c = 5% in 5 M HCl
Verunreinigungen
insoluble matter, passes filter test
≤0.3% foreign amino acids
Glührückstand
≤0.05% (as SO4)
Verlust
≤0.1% loss on drying, 110 °C
Farbe
white
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Löslichkeit
1 M HCl: 0.5 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless
Anionenspuren
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 mg/kg
sulfate (SO42-): ≤150 mg/kg
Kationenspuren
Al: ≤5 mg/kg
As: ≤0.1 mg/kg
Ba: ≤5 mg/kg
Bi: ≤5 mg/kg
Ca: ≤10 mg/kg
Cd: ≤5 mg/kg
Co: ≤5 mg/kg
Cr: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
K: ≤50 mg/kg
Li: ≤5 mg/kg
Mg: ≤5 mg/kg
Mn: ≤5 mg/kg
Mo: ≤5 mg/kg
NH4+: ≤200 mg/kg
Na: ≤100 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Sr: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
λ
0.5 M in 1 M HCl
UV-Absorption
λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.20
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.10
SMILES String
N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1
InChIKey
CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N
Angaben zum Gen
human ... CA1(759) , CA2(760)
rat ... Grin2a(24409)
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
- als Metabolit zur Untersuchung der Enzym-Metabolit-Interaktionen im zentralen Stoffwechsel von Escherichia coli mittels kernmagnetischer Resonanz (NMR)
- in der Transmissionselektronenmikroskopie
- als Bestandteil von Komplettmedien für die Zucht von Hefestämmen
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.