919233
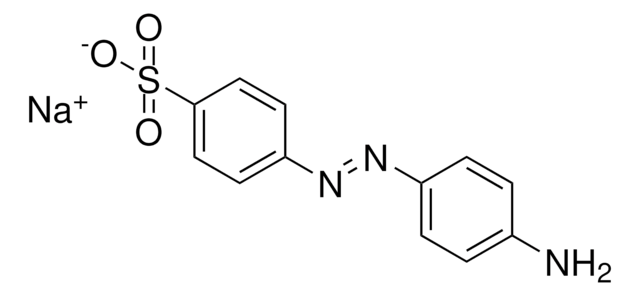
Sodium 2-(4-hexylphenyl)diazene-1-sulfonate
(0.5% solution in 25mM aqueous ammonium bicarbonate, pH 7.0), ≥95%
Synonym(e):
4-Hexylphenylazosulfonate, Azo
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
Empirische Formel (Hill-System):
C12H17N2O3S · Na
CAS-Nummer:
Molekulargewicht:
292.33
UNSPSC-Code:
12161503
NACRES:
NA.22
Empfohlene Produkte
Anwendung
4-Hexylphenylazosulfonate (Azo) is a photocleavable anionic surfactant developed by the Ge lab for use in high-throughput top-down and bottom-up proteomics by mass spectrometry (MS). Initially, the reagent showed a breakthrough as an improved method for top-down analysis [Brown et al. 2019]. Top-down analysis looks at intact proteins, while bottom-up analysis uses digested proteins. Of the two, top-down analysis is preferable for detecting post-translational modifications and sequence variations. Bottom-up is more commonly used and is likely to detect more proteins. This reagent was also shown to work for sample extraction that can be used for both top-down and bottom-up analysis on the same sample to maximize data collection[Brown et al. 2020].
Surfactants are required for protein extraction especially for challenging classes of protein including membrane proteins[Brown et al. 2020] and extracellular matrix proteins[Knott et al. 2020], but surfactants suppress the signal in MS. While removing a surfactant will improve the signal, this can cause protein loss and degradation. Azo allows for easy removal since it can be rapidly degraded using ultraviolet irradiation (λmax = 305 nm). Using Azo in this way reduces protein loss and gives an improved signal. Please see the Ge lab publications for information on using this product [Brown et al. 2019, Brown et al. 2020, Knott et al. 2020, and Aballo et al. 2021].
Product can be used with our line of photoreactors: Including Penn PhD (Z744035) & SynLED 2.0 (Z744080)
Surfactants are required for protein extraction especially for challenging classes of protein including membrane proteins[Brown et al. 2020] and extracellular matrix proteins[Knott et al. 2020], but surfactants suppress the signal in MS. While removing a surfactant will improve the signal, this can cause protein loss and degradation. Azo allows for easy removal since it can be rapidly degraded using ultraviolet irradiation (λmax = 305 nm). Using Azo in this way reduces protein loss and gives an improved signal. Please see the Ge lab publications for information on using this product [Brown et al. 2019, Brown et al. 2020, Knott et al. 2020, and Aballo et al. 2021].
Product can be used with our line of photoreactors: Including Penn PhD (Z744035) & SynLED 2.0 (Z744080)
Rechtliche Hinweise
PCT/US2019/035447
Lagerklassenschlüssel
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Leider sind derzeit keine COAs für dieses Produkt online verfügbar.
Wenn Sie Hilfe benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an Kundensupport
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Photocleavable Surfactant-Enabled Extracellular Matrix Proteomics.
Knott S J, et al.
Analytical Chemistry, 92(24), 15693-15698 (2020)
Kyle A Brown et al.
Nature methods, 16(5), 417-420 (2019-04-17)
We report the identification of a photocleavable anionic surfactant, 4-hexylphenylazosulfonate (Azo), which can be rapidly degraded by ultraviolet irradiation, for top-down proteomics. Azo can effectively solubilize proteins with performance comparable to that of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and is compatible
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.