Wichtige Dokumente
XTGHP-RO
Roche
X-tremeGENE™ HP DNA-Transfektionsreagenz
High-performance polymer reagent for transfecting many cell lines
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
Molecular Biology
for molecular biology
Qualitätsniveau
Form
liquid (aqueous solution)
Verwendung
mL (suitable for 165 transfections)
Verpackung
pkg of 0.4 mL (06366244001)
pkg of 1.0 mL (06366236001)
pkg of 5 × 1 mL (06366546001)
Hersteller/Markenname
Roche
Methode(n)
transfection: suitable
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Verwandte Kategorien
Allgemeine Beschreibung
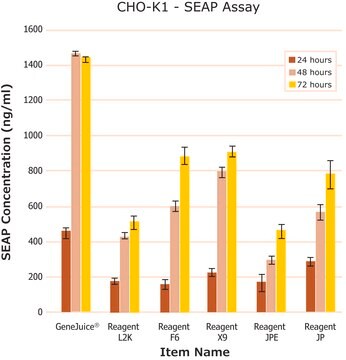
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
- Nutzen Sie die Vorteile eines einfach anzuwendenden nicht-liposomalen Reagenzes, das keine aus Tieren gewonnenen Bestandteile enthält, bei Raumtemperatur haltbar ist, durch eine 0,2-μm-Membran filtriert wurde und in serumhaltigem Medium aktiv ist.
- Erzielen Sie eine bisher unerreichte Effizienz bei der Transfektion von Primärzellen und Tumorzelllinien, die sich durch andere Reagenzien nur schwer transfizieren lassen.
- Generieren Sie physiologisch relevante Daten mit einem Reagenz mit geringen zytotoxischen Wirkungen.
- Erhöhen Sie Ihren Versuchsdurchsatz und ermöglichen Sie Targetbewertungen unter Anwendung eines einfachen und einheitlichen Protokolls.
Qualität
Physikalische Form
Sonstige Hinweise
Rechtliche Hinweise
Ähnliches Produkt
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 2
Lagerklassenschlüssel
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
334.4 °F
Flammpunkt (°C)
168 °C
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Automation is used for many applications to reduce variation caused by manual handling and to obtain reproducible results in high-throughput assays. High-throughput applications, such as knockdown studies or target screenings, often include cell transfection.
Small inhibitory RNAs (siRNAs) have become the focus of interest in many laboratories. For the first time, these molecules offer an easy way to knock down the expression of selected genes in mammalian cells without having to resort to classical gene knockout techniques.
Transfection is the introduction of DNA, RNA, or proteins into eukaryotic cells and is used in research to study and modulate gene expression. Thus, transfection techniques and protocols serve as an analytical tool that facilitates the characterization of genetic functions, protein synthesis, cell growth and development.
This brief webinar provides an overview of what transfection is and the methods that are used to introduce DNA or RNA into eukaryotic cells.
Protokolle
Lentiviruses represent a powerful tool in research applications to transduce a wide range of cell types.
Cell preparation for transfection Plate cells approx. 24 hours before transfection making sure cells are at optimal concentration (70 – 90 % confluency).
Transient co-transfection of plasmids is a method that is commonly employed for cellular protein-protein interaction studies, transcription factor studies, and gene knockdown studies using shRNA encoding plasmids.
Protocols for Transfecting Common Cell Lines with X-tremeGENE™ Transfection Reagents
Verwandter Inhalt
Browse our convenient transfection reagent selection guide to match the best reagent for your specific cell line and application needs.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.