17-10195
ProteoExtract® Anreicherungs- und Isolierungskit für das Zytoskelett
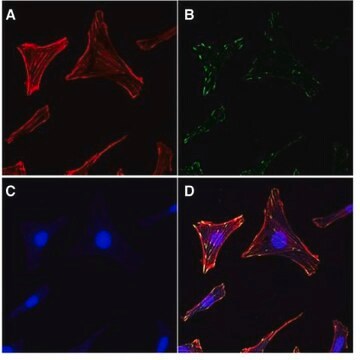
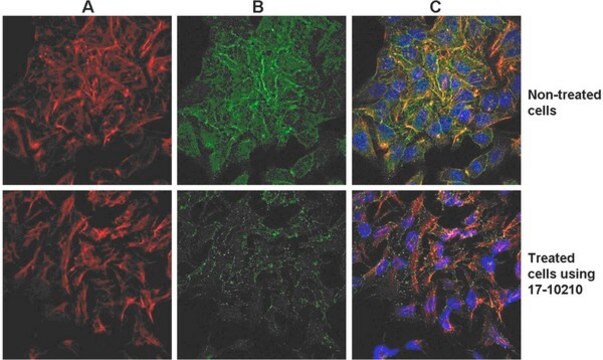
This kit provides cytoskeleton purification detergent buffers, sufficient for extraction from ten 100 mm culture dishes, that retain focal adhesion & actin-associated proteins while removing soluble cytoplasmic & nuclear proteins from the cell.
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC-Code:
12161503
eCl@ss:
32161000
Empfohlene Produkte
Hersteller/Markenname
Chemicon®
ProteoExtract®
Methode(n)
western blot: suitable
Versandbedingung
dry ice
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Read our application note in Nature Methods!
http://www.nature.com/app_notes/nmeth/2012/121007/pdf/an8624.pdf
(Click Here!)
Rediscovering the Actin Cytoskeleton: New techniques leading to discoveries in cell migration, Dr. Richard Klemke, Morris Cancer Center, UCSD, USA.
The actin cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic network composed of actin polymers and a large variety of associated proteins. The functions of the actin cytoskeleton is to mediate a variety of essential biological functions in all eukaryotic cells, including intra- and extra-cellular movement and structural
Support (Chen, C.S., et al., 2003; Frixione E., 2000). To perform these functions, the organization of the actin cytoskeleton must be tightly regulated both temporally and spatially. Many proteins associated with the actin cytoskeleton are thus likely targets of signaling pathways controlling actin assembly. Actin cytoskeleton assembly is regulated at multiple levels, including the organization of actin monomers (G-actin) into actin polymers and the superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network (F-actin – the major constituent of microfilaments) (Bretscher, A., et al., 1994). This superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network is mediated by actin side-binding or cross-linking proteins (Dubreuil, R. R., 1991; Matsudaira, P., 1991; Matsudaira, P., 1994). The actin cytoskeleton is a dynamic structure that rapidly changes shape and organization in response to stimuli and cell cycle progression. Therefore, a disruption of its normal regulation may lead to cell transformations and cancer. Transformed cells have been shown to contain less F-actin than untransformed cells and exhibit atypical coordination of F-actin levels throughout the cell cycle (Rao, J.Y., et al., 1990). Orientational distribution of actin filaments within a cell is, therefore, an important determinant of cellular shape and motility.
Focal adhesion and adherens junctions are membrane-associated complexes that serve as nucleation sites for actin filaments and as cross-linkers between the cell exterior, plasma membrane and actin cytoskeleton (Yamada, K.M., Geiger, B., 1997). The function of focal adhesions is structural, linking the ECM on the outside to the actin cytoskeleton on the inside. They are also sites of signal transduction, initiating signaling pathways in response to adhesion. Focal adhesions consist of integrin-type receptors that are attached to the extracellular matrix and are intracellularly associated with protein complexes containing vinculin (universal focal adhesion marker), talin, α-actinin, paxillin, tensin, zyxin and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) (Burridge, K., et al., 1990; Turner, C.E., Burridge, K., 1991).
Studying the proteins that associate with and regulate the actin cytoskeleton has been traditionally difficult because of the insolubility of the cytoskeleton in traditional detergents like Triton-X100. Work over the years has shown that many actin regulatory proteins/phospho-proteins upon activation move from the soluble cytoplasmic compartment to the insoluble actin cytoskeleton. The insolubility of these important proteins has made it difficult to study their biochemical changes, such as phosphorylation and nitrosylation, upon binding to actin. What is sorely needed is a cytoskeleton purification method that allows for the selective enrichment of cytoskeleton-associated proteins for detailed protein biochemical analyses. Such a method would provide the means to directly study this important pool of proteins in normal and diseased cytoskeletons.
http://www.nature.com/app_notes/nmeth/2012/121007/pdf/an8624.pdf
(Click Here!)
Rediscovering the Actin Cytoskeleton: New techniques leading to discoveries in cell migration, Dr. Richard Klemke, Morris Cancer Center, UCSD, USA.
The actin cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic network composed of actin polymers and a large variety of associated proteins. The functions of the actin cytoskeleton is to mediate a variety of essential biological functions in all eukaryotic cells, including intra- and extra-cellular movement and structural
Support (Chen, C.S., et al., 2003; Frixione E., 2000). To perform these functions, the organization of the actin cytoskeleton must be tightly regulated both temporally and spatially. Many proteins associated with the actin cytoskeleton are thus likely targets of signaling pathways controlling actin assembly. Actin cytoskeleton assembly is regulated at multiple levels, including the organization of actin monomers (G-actin) into actin polymers and the superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network (F-actin – the major constituent of microfilaments) (Bretscher, A., et al., 1994). This superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network is mediated by actin side-binding or cross-linking proteins (Dubreuil, R. R., 1991; Matsudaira, P., 1991; Matsudaira, P., 1994). The actin cytoskeleton is a dynamic structure that rapidly changes shape and organization in response to stimuli and cell cycle progression. Therefore, a disruption of its normal regulation may lead to cell transformations and cancer. Transformed cells have been shown to contain less F-actin than untransformed cells and exhibit atypical coordination of F-actin levels throughout the cell cycle (Rao, J.Y., et al., 1990). Orientational distribution of actin filaments within a cell is, therefore, an important determinant of cellular shape and motility.
Focal adhesion and adherens junctions are membrane-associated complexes that serve as nucleation sites for actin filaments and as cross-linkers between the cell exterior, plasma membrane and actin cytoskeleton (Yamada, K.M., Geiger, B., 1997). The function of focal adhesions is structural, linking the ECM on the outside to the actin cytoskeleton on the inside. They are also sites of signal transduction, initiating signaling pathways in response to adhesion. Focal adhesions consist of integrin-type receptors that are attached to the extracellular matrix and are intracellularly associated with protein complexes containing vinculin (universal focal adhesion marker), talin, α-actinin, paxillin, tensin, zyxin and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) (Burridge, K., et al., 1990; Turner, C.E., Burridge, K., 1991).
Studying the proteins that associate with and regulate the actin cytoskeleton has been traditionally difficult because of the insolubility of the cytoskeleton in traditional detergents like Triton-X100. Work over the years has shown that many actin regulatory proteins/phospho-proteins upon activation move from the soluble cytoplasmic compartment to the insoluble actin cytoskeleton. The insolubility of these important proteins has made it difficult to study their biochemical changes, such as phosphorylation and nitrosylation, upon binding to actin. What is sorely needed is a cytoskeleton purification method that allows for the selective enrichment of cytoskeleton-associated proteins for detailed protein biochemical analyses. Such a method would provide the means to directly study this important pool of proteins in normal and diseased cytoskeletons.
Anwendung
Das EMD Millipore ProteoExtract® Zytoskelett-Anreicherungs- und Isolierungskit stellt Zytoskelett-Aufreinigungsdetergenspuffer in ausreichender Menge für zehn 100-mm-Kulturschalen bereit, welche die Fokaladhäsion und Aktin-assoziierte Proteine erhalten, während sie lösliche Zytoplasma- und Zellkernproteine aus der Zelle entfernen. Die Anti-Vimentin- und Anti-GAPDH-Antikörper werden als Marker für das Zytoskelett bzw. Zytosol in Western Blot bereitgestellt. Dieses Kit steigert die Fähigkeit, Aktin-assoziierte Proteine mit geringem Vorkommen, die in konventionellen Verfahren der Western-Blot-Analyse von Ganzzelllysaten in der Regel maskiert sind, nachzuweisen und zu untersuchen.
Dieses Kit stellt Zytoskelett-Aufreinigungsdetergenspuffer in ausreichender Menge für zehn 100-mm-Kulturschalen bereit, welche die Fokaladhäsion und Aktin-assoziierte Proteine erhalten, während sie lösliche Zytoplasma- und Zellkernproteine aus der Zelle entfernen.
Forschungs-Unterkategorie
Zytoskelett
Zytoskelett
Forschungskategorie
Zellstruktur
Zellstruktur
Verpackung
Ausreichend Reagenzien für 15 Reaktionen/Isolierungen
Komponenten
Eine Flasche mit 1,9 ml 10X-Zellextraktionspuffer
Eine Flasche mit 3,5 ml 20X-Zytoskelettwaschpuffer
Eine Flasche mit 9 ml gebrauchsfertigem Zellkernextraktionspuffer
Zwei Fläschchen mit je 100 μl 1000X-Proteaseinhibitor-Cocktail-Lösung
Ein Fläschchen mit 150 μl 1000X-Natriumorthovanadat-Lösung
Eine Flasche mit 3,8 ml gebrauchsfertigem Zytoskelettsolubilisierungspuffer
Ein Fläschchen mit 30 µl 2000X-Anti-Maus-Antikörper der Ziege, HRP-Konjugat
Ein Fläschchen mit 50 µl monoklonalem 1000X-Anti-GAPDH-Maus-IgG1-Antikörper
Ein Fläschchen mit 100 µl monoklonalem 500X-Anti-Vimentin-Maus-IgG-Antikörper
Eine Flasche mit 3,5 ml 20X-Zytoskelettwaschpuffer
Eine Flasche mit 9 ml gebrauchsfertigem Zellkernextraktionspuffer
Zwei Fläschchen mit je 100 μl 1000X-Proteaseinhibitor-Cocktail-Lösung
Ein Fläschchen mit 150 μl 1000X-Natriumorthovanadat-Lösung
Eine Flasche mit 3,8 ml gebrauchsfertigem Zytoskelettsolubilisierungspuffer
Ein Fläschchen mit 30 µl 2000X-Anti-Maus-Antikörper der Ziege, HRP-Konjugat
Ein Fläschchen mit 50 µl monoklonalem 1000X-Anti-GAPDH-Maus-IgG1-Antikörper
Ein Fläschchen mit 100 µl monoklonalem 500X-Anti-Vimentin-Maus-IgG-Antikörper
Lagerung und Haltbarkeit
Bewahren Sie die ungeöffneten Kit-Module (17-10195-1 und 17-10195-2) bei den angegebenen Temperaturen auf. Das Kit kann bis zu 4 Monate nach Erhalt verwendet werden, Wiederholte Einfrier-/Auftauzyklen vermeiden und bei Bedarf aliquotieren.
Rechtliche Hinweise
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
PROTEOEXTRACT is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Haftungsausschluss
Sofern in unserem Katalog oder anderen Begleitdokumenten unserer Produkte nicht anders angegeben, sind unsere Produkte nur für Forschungszwecke vorgesehen und nicht für andere Zwecke zu verwenden, einschließlich, jedoch nicht beschränkt auf unautorisierte kommerzielle Verwendung, zur In-vitro-Diagnostik, für Ex-vivo- oder In-vivo-Therapiezwecke oder jegliche Art der Einnahme oder Anwendung bei Menschen oder Tieren.
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
10 - Combustible liquids
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Viorica L Lastun et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 298(6), 101935-101935 (2022-04-19)
In metazoans, the architecture of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) differs between cell types and undergoes major changes throughout the cell cycle and according to physiological needs. Although much is known about how the different ER morphologies are generated and maintained
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.