Wichtige Dokumente
911410
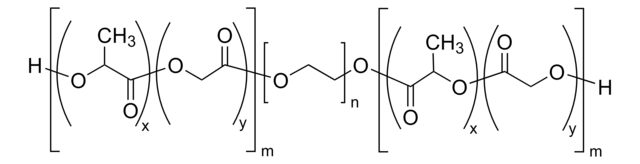
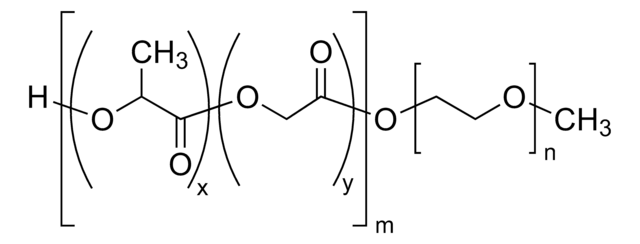
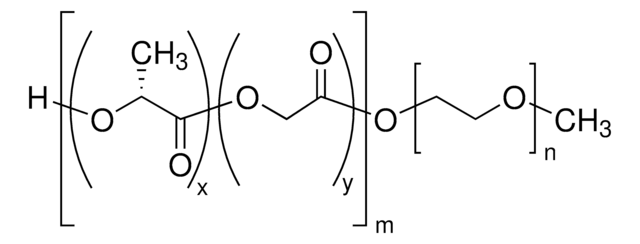
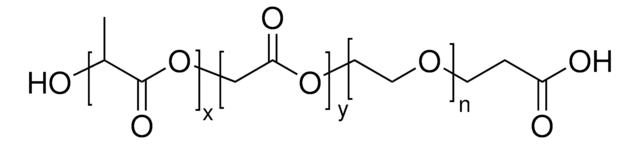
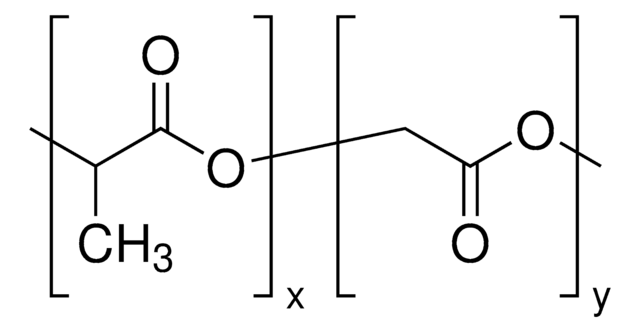
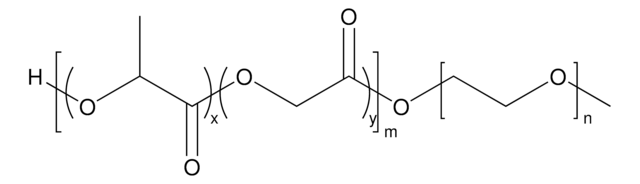
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether-block-poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
PEG average Mn 5,000, PLGA average Mn 10,000, lactide:glycolide 80:20
Synonym(e):
PEG-PLGA, PEG5K-PLGA10K, Polyethylene glycol, mPEG-b-PLGA
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Form
powder
Zufuhrverhältnis
lactide:glycolide 80:20
Mol-Gew.
PEG average Mn 5,000 (by NMR)
PLGA average Mn 10,000 (by NMR)
Verunreinigungen
≤500 ppm (GC)
Farbe
white
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Dokumente section.
Wenn Sie Hilfe benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an Kundensupport
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Artikel
Professor Robert K. Prud’homme introduces flash nanoprecipitation (FNP) for nanoparticle fabrication, which is a scalable, rapid mixing process for nanoparticle formulations.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.