430471
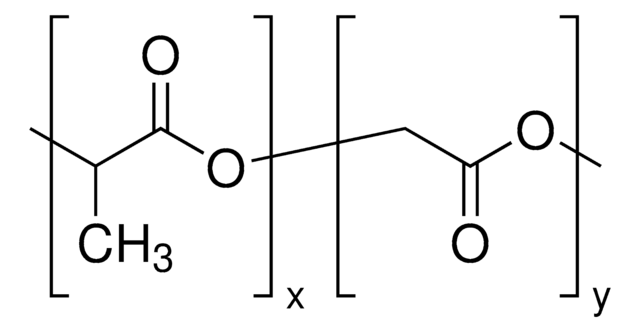
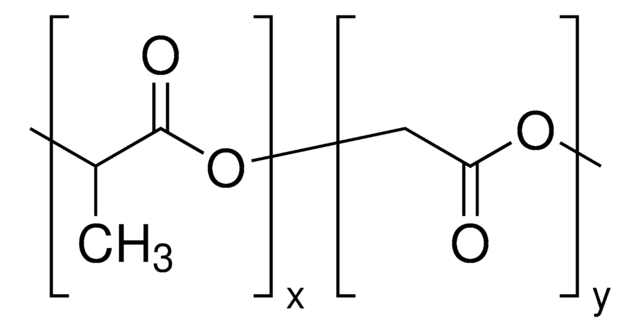
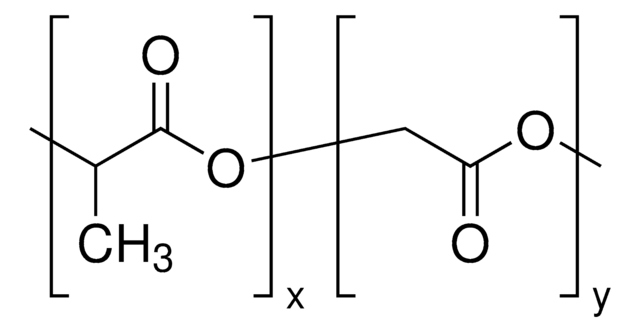
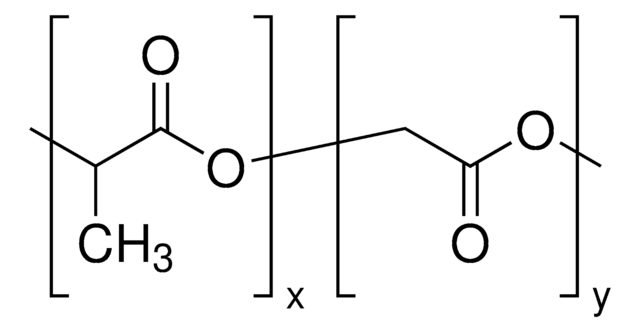
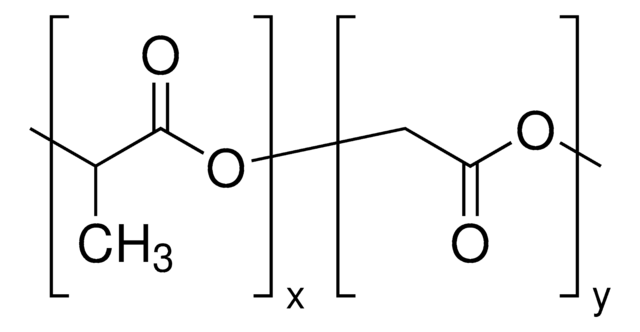
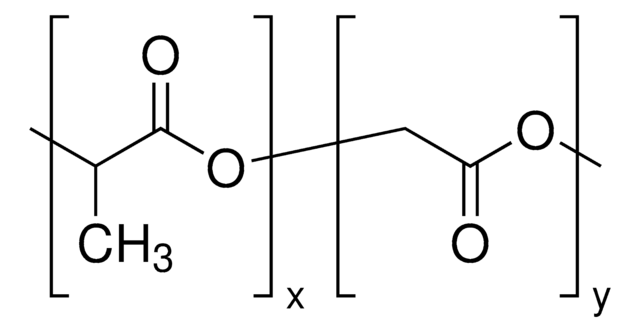
Poly(D,L-lactid-co-glycolid)
ester terminated, Mw 50,000-75,000
Synonym(e):
PLGA
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Form
amorphous
Zufuhrverhältnis
lactide:glycolide 85:15
Mol-Gew.
Mw 50,000-75,000
Zeitrahmen für den Abbau
<6 months
Viskosität
0.55-0.75 dL/g, 0.1 % (w/v) in chloroform(25 °C)
Übergangstemp.
Tg 45-50 °C
Löslichkeit
ethyl acetate, chloroform, acetone and THF: soluble
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
OCC(O)=O.CC(O)C(O)=O
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
Physikalische Form
Rechtliche Hinweise
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Interest in utilizing biodegradable polymers for biomedical applications has grown since the 1960s.
The world of commercial biomaterials has stagnated over the past 30 years as few materials have successfully transitioned from the bench to clinical use. Synthetic aliphatic polyesters have continued to dominate the field of resorbable biomaterials due to their long history and track record of approval with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.