Alle Fotos(1)
Wichtige Dokumente
284335
1,3-Dinitropyren
99%
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
Empirische Formel (Hill-System):
C16H8N2O4
CAS-Nummer:
Molekulargewicht:
292.25
MDL-Nummer:
UNSPSC-Code:
12352100
PubChem Substanz-ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Empfohlene Produkte
Assay
99%
Form
solid
Löslichkeit
DMSO: soluble 2 mg/mL, clear, yellow to orange
Funktionelle Gruppe
nitro
SMILES String
[O-][N+](=O)c1cc([N+]([O-])=O)c2ccc3cccc4ccc1c2c34
InChI
1S/C16H8N2O4/c19-17(20)13-8-14(18(21)22)12-7-5-10-3-1-2-9-4-6-11(13)16(12)15(9)10/h1-8H
InChIKey
KTNUVDBUEAQUON-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Verwandte Kategorien
Allgemeine Beschreibung
The carcinogenecity of 1,3-dinitropyrene was studied in newborn female rats.
Anwendung
1,3-Dinitropyrene has been used in:
- modification of the umu-assay (ISO 13829) to assess the cytotoxic potential of toxins
- in vitro synthesis of 1,N6-etheno-2′-deoxyadenosine and 1,N2-etheno-2′-deoxyguanosine
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
L B Tee et al.
Carcinogenesis, 9(10), 1869-1874 (1988-10-01)
Dinitropyrenes are mutagenic and carcinogenic environmental pollutants commonly found in diesel exhaust and airborne particulates. In the present study, the ability of rabbit lung to metabolize 1,8-dinitro[4,5,9,10-3H]pyrene by both oxygen-dependent and oxygen-independent pathways has been investigated. Using lung 9000 g
H Lee et al.
Mutation research, 324(1-2), 77-84 (1994-06-01)
The disposal of massive quantities of synthetic materials has become a very serious environmental problem around the world. When synthetic polymers are burnt or smolder in air, the combustion products are extremely complex, often consisting of several hundred compounds. In
A K Hajos et al.
Journal of biochemical toxicology, 6(4), 277-282 (1991-01-01)
The effect of highly purified rat liver cytosolic NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase [EC 1.6.99.2] on the mutagenicity of 1,3- 1,6- and 1,8-dinitropyrene (DNP) was studied in the Ames Salmonella typhimurium mutagenicity assay. NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase over the range of 0.02-0.8 micrograms/plate (38-1500) units
G W Winston et al.
Mutation research, 279(4), 289-298 (1992-06-16)
The effects of chronic ethanol feeding of rats on the ability of liver fractions to modulate the bacterial mutagenicity of three dinitropyrene isomers (1,3-, 1,6- and 1,8-DNP), which require bacterial enzymes but not an exogenous enzyme source for activation, were
C A Norman et al.
Carcinogenesis, 10(7), 1323-1327 (1989-07-01)
Formation of DNA adducts, following treatment of primary rabbit tracheal epithelial cells (RTEC) with 1,8-dinitropyrene (1,8-DNP) and its partially reduced derivative, 1-nitro-8-nitrosopyrene (1,8-NONO2), was examined using the 32P-post-labelling technique. Treatment of aerobic cells with 1,8-DNP or 1,8-NONO2 produced qualitatively similar
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.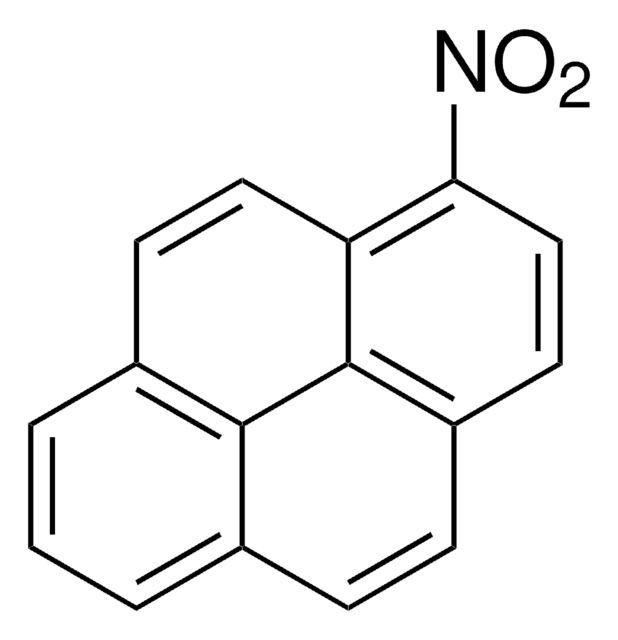
![1-(6-Methoxybenzo[d] thiazol-2-yl)hydrazine AldrichCPR](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/210/241/0c5be390-b73a-436d-82c7-c51156617e66/640/0c5be390-b73a-436d-82c7-c51156617e66.png)