155721
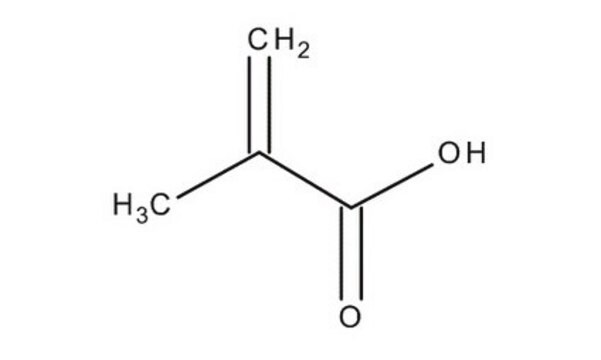
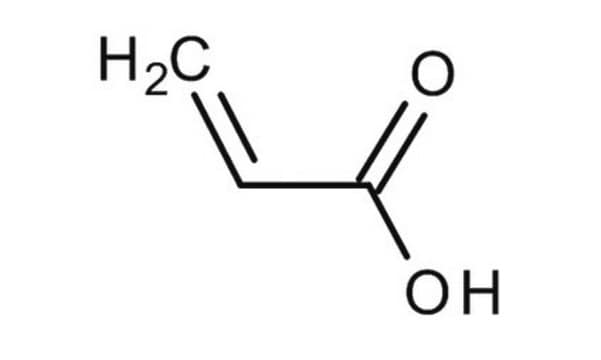
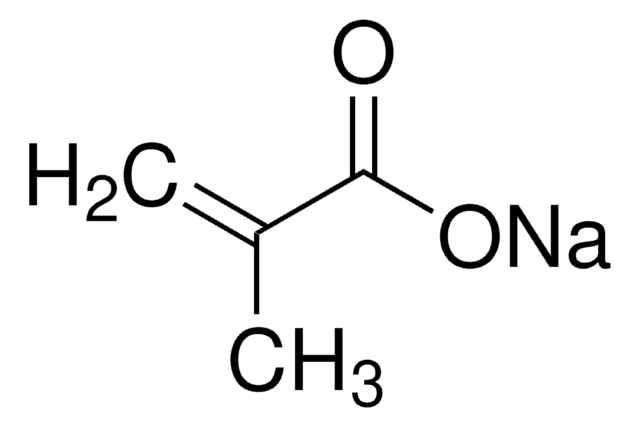
Methacrylsäure
contains 250 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor, 99%
Synonym(e):
2-Methacrylsäure, 2-Methylpropensäure
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Dampfdichte
>3 (vs air)
Qualitätsniveau
Dampfdruck
1 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Assay
99%
Form
liquid
Selbstzündungstemp.
752 °F
Enthält
250 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
Brechungsindex
n20/D 1.431 (lit.)
pH-Wert
2.0-2.2 (20 °C, 100 g/L)
bp
163 °C (lit.)
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
12-16 °C (lit.)
Dichte
1.015 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES String
C=C(C)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H6O2/c1-3(2)4(5)6/h1H2,2H3,(H,5,6)
InChIKey
CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1A - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Respiratory system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
152.6 °F - closed cup
Flammpunkt (°C)
67 °C - closed cup
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
(RAFT) Polymerization
Composites
Artikel
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
By altering the physicochemical properties, smart or intelligent drug delivery systems can be designed to deliver therapeutic molecules on-demand. Learn more about the application of stimuli-responsive materials in drug delivery.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.