T4455
TEV Protease
Synonym(s):
P1 protease, TEVp, Tobacco Etch Virus protease, rTEV
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
microbial (Tobacco Etch virus)
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
description
Contains both a histidine tag and a GST tag
form
solution
specific activity
≥3,000 units/mg protein
mol wt
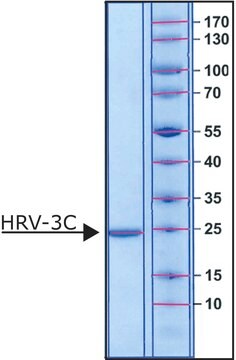
27 kDa
technique(s)
protein purification: suitable
suitability
suitable for purification of HIS tagged recombinant proteins
application(s)
genomic analysis
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Physical properties
Unit Definition
Physical form
Preparation Note
Prepare fresh dialysis buffer. Dialysis buffer should be optimized for target protein solubility and contain no protease inhibitors. The dialysis buffer should also be compatible with downstream purification processes, e.g. minimal amount of EDTA or DTT if a HIS Select® column will be used to remove the cleaved His-tag.
Example of suitable dialysis buffer; 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 150 - 500 mM NaCl, 14 mM β-mercaptoethanol
This TEV protease has the same activity in 150 mM NaCl or 500 mM NaCl and 400 mM imidazole.
Dilute the target protein sample to 1-2 mg/ml with dialysis buffer. This is optional in case the target protein aggregates in dialysis buffer. Save a small aliquot as a control for PAGE analysis. EDTA may be added to 0.5 mM final concentration if the target protein will be eluted from the HIS Select™ column and EDTA is compatible with the target protein.
Add TEV protease at a protease to target protein ratio of 1:100 (w/w) or 10,000 unit (1 mg) TEV protease to 100 mg of target protein. There is no need to calculate the molar ratio. TEV protease can be added directly to the target protein. There is no need to change buffer or dilute TEV protease. The optimal ratio should be determined empirically. A Protease-to-target protein ratio (w/w) of 1:50 to 1:200 should provide an affective range for most target proteins.
Dialyze against the dialysis buffer at 4 °C ~ 16 hrs. Dialysis is intended to remove imidazole or glutathione if HIS Select® or glutathione affinity columns are used to remove the cleaved tag or TEV protease after cleavage.
Typically, 1 mg of TEV protease will cleave >90% of 100mg of a control protein at 4 °C in 16 hours.
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Read our article about how the Nanodisc system allows for structural studies of membrane proteins.
This page shows how to perform a purification of His-tagged membrane proteins.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service