SAB4200730
Anti-Connexin 43 Antibody
mouse monoclonal, CXN-6
Synonym(s):
Anti-AVSD3, Anti-CMDR, Anti-CX43, Anti-EKVP, Anti-EKVP3, Anti-GJAL, Anti-HLHS1, Anti-HSS, Anti-ODDD, Anti-PPKCA
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Anti-Connexin 43 antibody, Mouse monoclonal, clone CXN-6, hybridoma cell culture supernatant
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
culture supernatant
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
CXN-6, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
species reactivity
chicken, rat, feline, bovine, human, porcine, mouse
packaging
antibody small pack of 25 μL
concentration
~1.0 mg/mL
technique(s)
immunoblotting: 1:5,000-1:7,500 using mouse myoblast C2C12 cell line extract
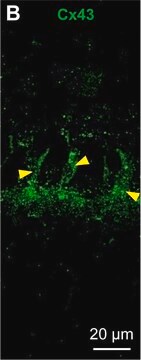
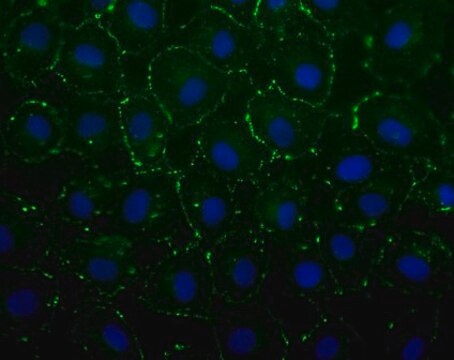
immunofluorescence: 1:500-1:1,000 using mouse myoblast C2C12 cell line
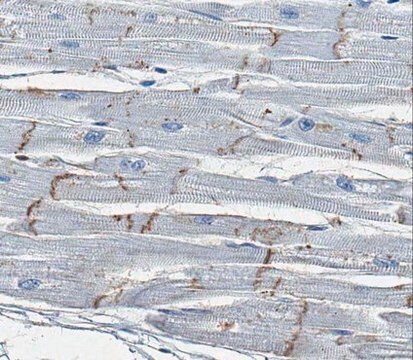
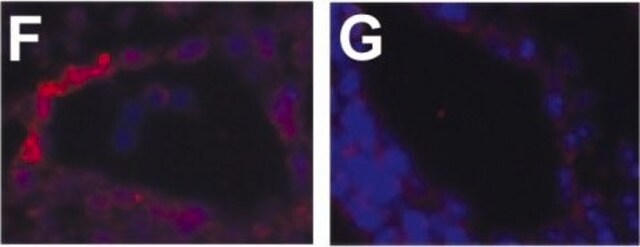
immunohistochemistry: 1:200-1:500 using heat-retrieved formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded mouse heart sections
isotype
IgM
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
bovine ... Gja1(281193)
cat ... Gja1(101100211)
chicken ... Gja1(395278)
human ... GJA1(2697)
mouse ... Gja1(14609)
rat ... Gja1(24392)
General description
Immunogen
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical form
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| SAB4200730-100UL | 4061837875816 |
| SAB4200730-25UL |
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service