H2125
Hemicellulase from Aspergillus niger
powder, 0.3-3.0 unit/mg solid (using a β-galactose dehydrogenase system and locust bean gum as substrate)
Synonym(s):
cellulase, mannanase, xylanase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(4)
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
powder
Quality Level
specific activity
0.3-3.0 unit/mg solid (using a β-galactose dehydrogenase system and locust bean gum as substrate)
greener alternative product characteristics
Waste Prevention
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
greener alternative category
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
We are committed to bringing you Greener Alternative Products, which adhere to one or more of The 12 Principles of Greener Chemistry. This product has been enhanced for energy efficiency and waste prevention when used in cellulosic ethanol research. For more information see the article in biofiles and Enzymes for Alternative Energy Research.
Application
Hemicellulase from Aspergillus niger has been used in enzyme digestions.
Biochem/physiol Actions
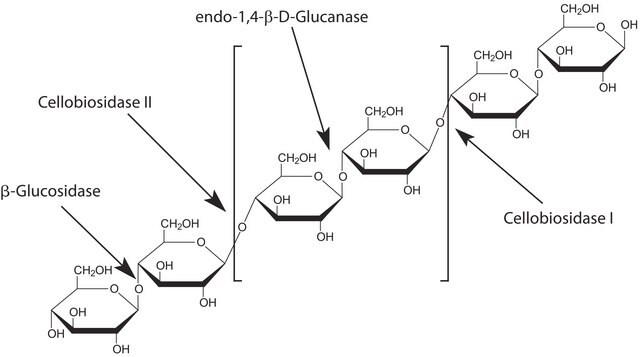
Hemicellulase is a group of enzymes that catalyzes the breakdown of heteropolysaccharides. It includes glucanases that act on glucan. Similarly, xylanases and mannanases breakdown xylan and mannan respectively. Hemicellulase is prevalent among various bacteria, fungi and plants.
Quality
An undefined mixture of glycolytic enzymes usually containing xylanase, mananase and other activities.
Unit Definition
One unit will produce a relative fluidity change of 1 per 5 minutes using locust bean gum as substrate at pH 4.5 at 40 °C
Other Notes
View more information on enzymes for complex carbohydrate analysis at www.sigma-aldrich.com/enzymeexplorer
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Domain-specific mechanosensory transmission of osmotic and enzymatic cell wall disturbances to the actin cytoskeleton
Wojtaszek P, et al.
Protoplasma, 230(3-4), 217-230 (2007)
Upgrading of residues of bracts, stems and hearts of Cynara cardunculus L. var. scolymus to functional fractions enriched in soluble fiber
Fissore EN, et al.
Food & Function, 5(3), 463-470 (2014)
Yanhua Dou et al.
Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 26(23) (2021-12-11)
Fungal pathogens have evolved combinations of plant cell-wall-degrading enzymes (PCWDEs) to deconstruct host plant cell walls (PCWs). An understanding of this process is hoped to create a basis for improving plant biomass conversion efficiency into sustainable biofuels and bioproducts. Here
Alondra M Idrovo Encalada et al.
Food chemistry, 289, 453-460 (2019-04-09)
Carrot residues were upgraded as pectin-enriched fractions (PEFs) useful for functional food formulation due to co-extracted antioxidants (α- and β-carotenes, lutein, α-tocopherol), and gelling effect. High power ultrasound (US)-enzyme assisted extraction was applied for efficiency and sustainability. Carrot powder (CP)
Eliana N Fissore et al.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 58(6), 3793-3800 (2010-02-25)
Chemical and rheological characteristics of fractions enriched in soluble dietary fiber are reported. These fractions were obtained through acid hydrolysis of butternut (Cucurbita moschata Duch ex Poiret) and red beet (Beta vulgaris L. var. conditiva) cell wall enriched powders. Hydrolysis
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service