C8649
Cholesterol Oxidase from Streptomyces sp.
lyophilized powder, ≥20 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
Cholesterol: oxygen oxidoreductase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(7)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Streptomyces sp.
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥20 units/mg protein
mol wt
~34 kDa
composition
protein, 55-65% biuret
solubility
50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0: soluble (Cold)
shipped in
dry ice
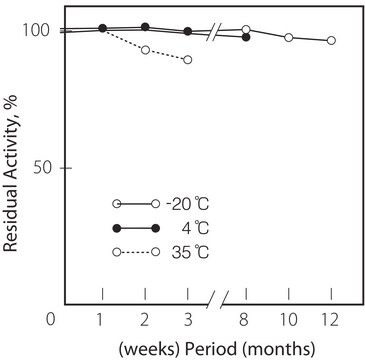
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Cholesterol Oxidase produced from Streptomyces sp corresponds to a molecular weight of 62 kDa. It has a pH and temperature optimum of 7 and 37 °C, respectively. Cholesterol Oxidase comprises a FAD-binding and a steroid-binding domain.
Application
Cholesterol oxidase from Streptomyces has been used in a study to assess the relationship between the micellar structure of model bile and the activity of esterase. Cholesterol oxidase from Streptomyces has also been used in a study to investigate the effects of sphingomyelin degradation on cell cholesterol oxidizability and steady-state distribution between the cell surface and the cell interior.
Cholesterol oxidase is used to determine serum cholesterol. The enzyme also finds application in the microanalysis of steroids in food samples and in distinguishing 3-ketosteroids from 3β-hydroxysteroids. Transgenic plants expressing cholesterol oxidase are being investigated in the fight against the cotton boll weevil. CHOD has also been used as a molecular probe to elucidate cellular membrane structures.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cholesterol Oxidase from microorganisms use cholesterol for carbon and energy. It is useful in diagnostic assays involving cholesterol, especially in lipid disorders. Cholesterol oxidase has an insecticidal property and aids protection against boll weevil larvae. The Streptomyces sp cholesterol oxidase has long shelf-life with good performance.
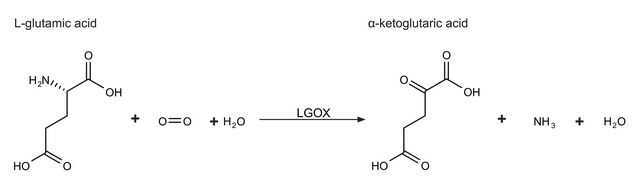
Cholesterol oxidase (CHOD) is a monomeric flavoprotein containing FAD that catalyzes the first step in cholesterol catabolism. This bifunctional enzyme oxidizes cholesterol to cholest-5-en-3-one in an FAD-requiring step, which is then isomerized to cholest-4-en-3-one with the release of H2O2.
Physical properties
Isoelectric point : 5.1 ± 0.1 and 5.4 ± 0.1
Michaelis constant : 4.3 x 10‾5M(Cholesterol)
Inhibitors : Ionic detergents, Hg++, Ag+
Optimum pH : 6.5 − 7.0
Optimum temperature : 45 – 50°C
pH Stability : pH 5.0 – 10.0 (25°C, 20hr)
Thermal stability : Below 45°C (pH 7.0, 15min)
Michaelis constant : 4.3 x 10‾5M(Cholesterol)
Inhibitors : Ionic detergents, Hg++, Ag+
Optimum pH : 6.5 − 7.0
Optimum temperature : 45 – 50°C
pH Stability : pH 5.0 – 10.0 (25°C, 20hr)
Thermal stability : Below 45°C (pH 7.0, 15min)
Unit Definition
One unit will convert 1.0 μmole of cholesterol to 4-cholesten-3-one per min at pH 7.5 at 25 °C. Note: 4-cholesten-3-one may undergo isomerization.
Physical form
lyophilized powder containing bovine serum albumin and amino acids as stabilizers
Preparation Note
CHOD is soluble in cold 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0. Prepare solutions immediately before use.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
J P Slotte et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 985(1), 90-96 (1989-10-02)
This study addresses questions related to (i) the distribution of cholesterol between the cell surface and intracellular membranes in cultured fibroblasts and (ii) the effects of plasma membrane sphingomyelin on this distribution. Cholesterol oxidase (Streptomyces sp.) converts cell cholesterol to
Crystal structure determination of cholesterol oxidase from Streptomyces and structural characterization of key active site mutants
Yue QK, et al.
Biochemistry, 38(14), 4277-4286 (1999)
Extracellular cholesterol oxidase production by Streptomyces aegyptia, in vitro anticancer activities against rhabdomyosarcoma, breast cancer cell-lines and in vivo apoptosis
NEA El-Naggar, et al.
Scientific reports, 8(1), 2706-2706 (2018)
Laura Caldinelli et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 280(24), 22572-22581 (2005-04-09)
Cholesterol oxidase from Brevibacterium sterolicum is a monomeric flavoenzyme catalyzing the oxidation and isomerization of cholesterol to cholest-4-en-3-one. This protein is a class II cholesterol oxidases, with the FAD cofactor covalently linked to the enzyme through the His(69) residue. In
Effect of cholesterol concentration on organization of viral and vesicle membranes. Probed by accessibility to cholesterol oxidase.
R Pal et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 255(12), 5802-5806 (1980-06-25)
Protocols
Assay Procedure for Cholesterol Oxidase
Enzymatic Assay of Cholesterol Oxidase
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service