About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
form
powder
composition
Peptide content, ~70%
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
storage temp.
−20°C
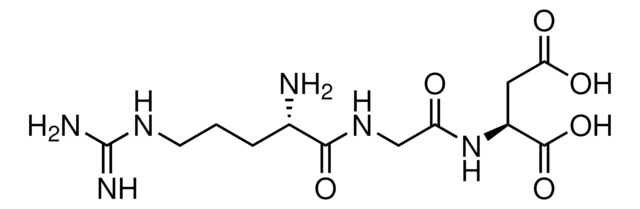
SMILES string
N[C@@H](CCCNC(N)=N)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C15H27N7O8/c16-7(2-1-3-19-15(17)18)12(27)20-5-10(24)21-8(4-11(25)26)13(28)22-9(6-23)14(29)30/h7-9,23H,1-6,16H2,(H,20,27)(H,21,24)(H,22,28)(H,25,26)(H,29,30)(H4,17,18,19)/t7-,8-,9-/m0/s1
InChI key
NNRFRJQMBSBXGO-CIUDSAMLSA-N
Gene Information
human ... ITGA2B(3674) , ITGB3(3690)
mouse ... Itgb3(16416)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
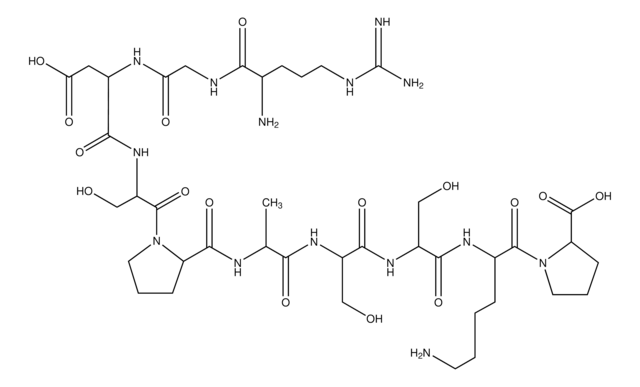
Amino Acid Sequence
General description
RGDS has been shown to block fibrinogen-induced aggregation of intact erythrocytes and specific binding of fibrinogen to erythrocyte membranes. The effect of RGDS on transforming growth factor ß1 (TGFß1) mRNA expression and secretion in cultured human mesangial cells has been investigated. RGDS has been utilized in a study of integrin-mediated signal transduction in cultured cells from the sponge Suberites domuncula. RGDS has been demonstrated
to mitigate the binding of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to murine alveolar macrophages
Application
- to study its effects on cell attachment in rats
- to analyse the interaction of fibrinogen with erythrocytes occurs through integrin related receptor
- to pretreat the cells, to assess the role of integrin in the cell attachment process
- to test its competition with platelet-secreted, nanosheet-adsorbed proteins for binding to glycoprotein IIIa (GPIIIa)
Packaging
Preparation Note
clear, colorless solution.
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Tissue engineering has become a key therapeutic tool in the treatment of damaged or diseased organs and tissues, such as blood vessels and urinary bladders.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service