ERMDA471IFCC
Human serum (cystatin C)
ERM®, certified reference material
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41116107
NACRES:
NA.24
Recommended Products
grade
certified reference material
Agency
ERM®
manufacturer/tradename
JRC
application(s)
clinical testing
format
matrix material
storage temp.
−70°C
General description
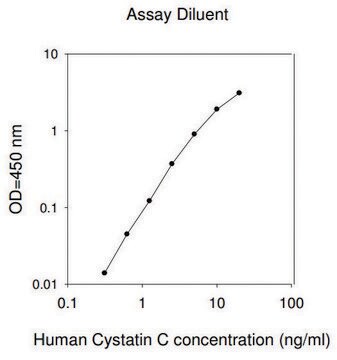
Certified for cystatin C in human serum.
ERM-DA471IFCC_cert
ERM-DA471IFCC_report
ERM-DA471IFCC_origin
ERM-DA471IFCC_cert
ERM-DA471IFCC_report
ERM-DA471IFCC_origin
Application
- Serum biomarker for sarcopenia: A study utilized the serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio as a biomarker for sarcopenia components among different age groups in older ndividuals, underscoring the role of human serum cystatin C in monitoring muscle health and potentially guiding interventions (Fang et al., 2024).
- Screening of sarcopenia: The investigation demonstrated the efficacy of using serum creatinine-cystatin C based screenings for sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults, highlighting cystatin C′s significance as a reliable indicator of muscle degradation, which is crucial for early intervention (Matsuzawa et al., 2024).
- Predictive tool in chronic kidney disease: Research emphasized native T1-mapping combined with human serum cystatin C levels as predictors of renal function decline in chronic kidney disease patients, illustrating cystatin Cs utility in enhancing the diagnosis and management of kidney disease (Shi et al., 2024).
Analysis Note
For more information please see:
ERMDA471/IFCC
ERMDA471/IFCC
Legal Information
ERM is a registered trademark of European Commission
Disclaimer
RESEARCH USE ONLY. This product is regulated in France when intended to be used for scientific purposes, including for import and export activities (Article L 1211-1 paragraph 2 of the Public Health Code). The purchaser (i.e. enduser) is required to obtain an import authorization from the France Ministry of Research referred in the Article L1245-5-1 II. of Public Health Code. By ordering this product, you are confirming that you have obtained the proper import authorization.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Aquatic Chronic 3
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Determination of Cystatin C in human serum by isotope dilution mass spectrometry using mass overlapping peptides.
Gonzalez-Antu?a A, et al.
Journal of Proteomics, 112, 141-155 (2015)
K Habiro et al.
American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, 9(6), 1324-1329 (2009-05-23)
Thymus xenotransplantation has been shown to induce tolerance to porcine xenografts in mice and to permit survival of alpha1,3Gal-transferase knockout porcine kidney xenografts for months in nonhuman primates. We evaluated the ability of porcine thymus xenotransplantation to induce human T-cell
Bin Ma et al.
Scientific reports, 1, 140-140 (2012-02-23)
Transport of mRNAs to diverse neuronal locations via RNA granules serves an important function in regulating protein synthesis within restricted sub-cellular domains. We recently detected the Huntington's disease protein huntingtin (Htt) in dendritic RNA granules; however, the functional significance of
Adriano Boasso et al.
Clinical immunology (Orlando, Fla.), 129(1), 132-144 (2008-07-25)
The programmed death (PD)-1 interacts with its ligand (PDL-1) delivering a negative signal to T cells. During human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 infection PD-1 and PDL-1 expressions are increased. Here we show that monocytes and CCR5(+) T cells of HIV-uninfected donors
Lynell W Klassen et al.
Biochemical pharmacology, 76(3), 426-436 (2008-07-05)
Alcohol abuse results in liver injury, but investigations into the mechanism(s) for this injury have been hampered by the lack of appropriate in vitro culture models in which to conduct in depth and specific studies. In order to overcome these
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service