11767291910
Roche
TUNEL Label Mix
sufficient for 30 tests, pkg of 3 × 550 μL
Synonym(s):
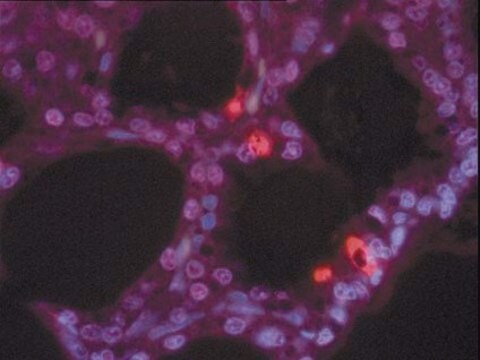
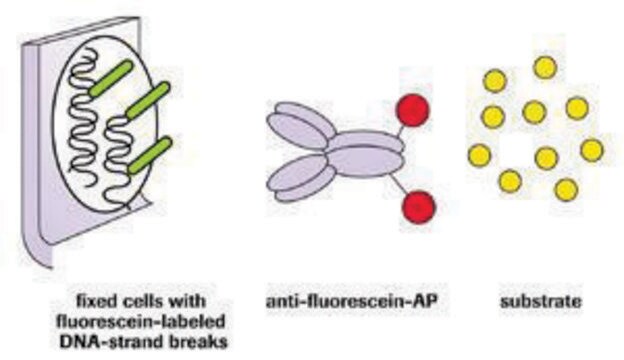
transferase dUTP nick end labeling, tunel
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
solution
Quality Level
usage
sufficient for 30 tests
packaging
pkg of 3 × 550 μL
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
color
colorless
solubility
water: miscible
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Application
Preparation Note
For one test: Mix 45 μl TUNEL Label with 5 μl TUNEL Enzyme prior to use. For negative control use 50 μl/test TUNEL Label only.
Storage conditions (working solution): Note: The TUNEL reaction mixture (45 μl TUNEL Label with 5 μl TUNEL Enzyme for 1 test) should be prepared just before use, and should not be stored. Keep the TUNEL reaction mixture on ice until use.
Other Notes
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Carc. 1B Inhalation
Storage Class Code
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
does not flash
Flash Point(C)
does not flash
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service