722995
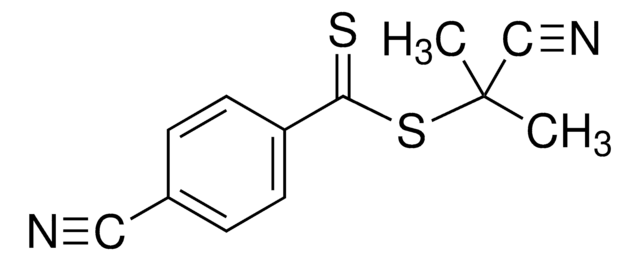
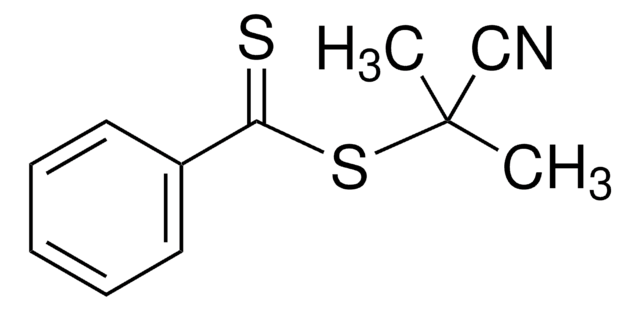
4-Cyano-4-(phenylcarbonothioylthio)pentanoic acid
Synonym(s):
4-Cyano-4-(thiobenzoylthio)pentanoic acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
powder
Quality Level
mp
94-98 °C
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
CC(CCC(O)=O)(SC(=S)c1ccccc1)C#N
InChI
1S/C13H13NO2S2/c1-13(9-14,8-7-11(15)16)18-12(17)10-5-3-2-4-6-10/h2-6H,7-8H2,1H3,(H,15,16)
InChI key
YNKQCPNHMVAWHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
Application
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
A series of polymerization were carried out using RAFT agents and monomers yielding well-defined polymers with narrow molecular weight distributions. The process allows radical-initiated growing polymer chains to degeneratively transfer reactivity from one to another through the use of key functional groups (dithioesters, trithiocarbonates, xanthates and dithiocarbamates). RAFT agents help to minimize out-of-control growth and prevent unwanted termination events from occurring, effectively controlling polymer properties like molecular weight and polydispersity. RAFT agents are commercially available. RAFT does not use any cytotoxic heavy metal components (unlike ATRP).
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Over the past two decades, the rapid advance of controlled living polymerization (CLP) techniques.
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Protocols
RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation chain Transfer) is a form of living radical polymerization involving conventional free radical polymerization of a substituted monomer in the presence of a suitable chain transfer (RAFT) reagent.
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)
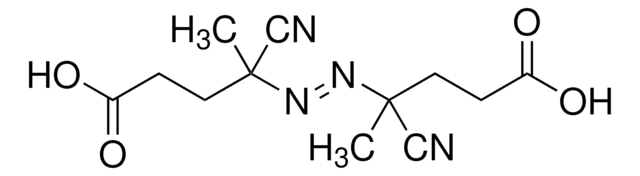
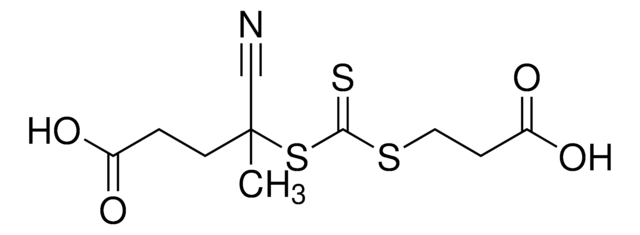
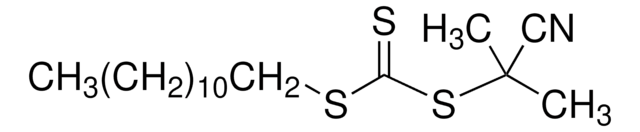
![2-[[(2-Carboxyethyl)sulfanylthiocarbonyl]-sulfanyl]propanoic acid](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/427/606/b02310e2-102e-4324-b09d-e4c0de4fab2c/640/b02310e2-102e-4324-b09d-e4c0de4fab2c.png)
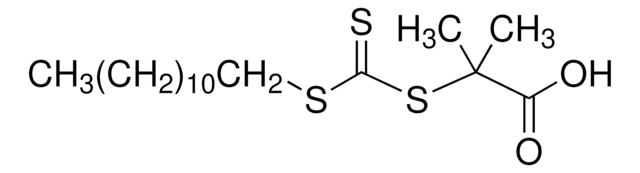
![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanol](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/839/520/64c23004-f340-460f-a379-8670a35d0433/640/64c23004-f340-460f-a379-8670a35d0433.png)