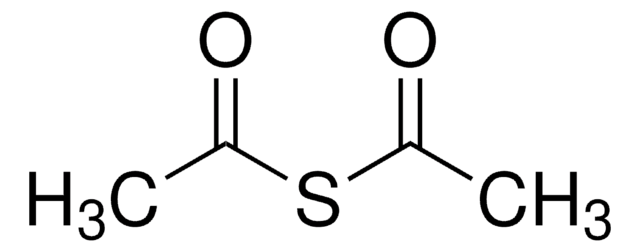
670359
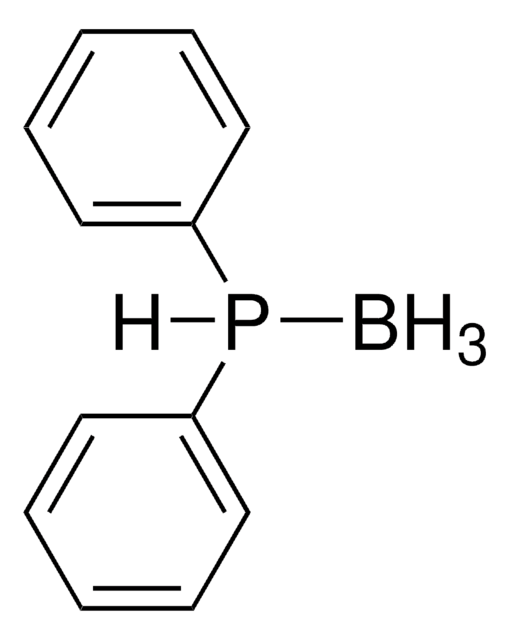
Acetylthiomethyl-diphenylphosphine borane complex
≥98.0%
Synonym(s):
(T-4)-[S-[(Diphenylphosphino-κP)methyl] ethanethioate]trihydroboron
About This Item
Recommended Products
Assay
≥98.0%
form
solid
reaction suitability
reaction type: click chemistry
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Staudinger Reaction
mp
52-55 °C
functional group
phosphine
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
B.CC(=O)SCP(c1ccccc1)c2ccccc2
InChI
1S/C15H15OPS.BH3/c1-13(16)18-12-17(14-8-4-2-5-9-14)15-10-6-3-7-11-15;/h2-11H,12H2,1H3;1H3
InChI key
MXPNVFCCEGQGEN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
- Traceless Staudinger ligation reagent with borane protecting group.
- The borane group stabilizes the phosphine against oxidation and can be easily removed with mild basic or acidic conditions to yield the active phosphine.
- After reaction with an azide, the phosphine is eliminated in the presence of water to yield a native amide bond.
- Used in the synthesis of cyclic peptides.

Packaging
Legal Information
related product
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Based on the same working principle as the nontraceless Staudinger Ligation the auxiliary phosphine reagent can be cleaved from the product after the ligation is completed leaving a native amide bond. Thus, the total chemical synthesis of proteins and glycopeptides is enabled overcoming the limitations of native chemical ligation (NCL) of a Cys residue at the ligation juncture.
Chemoselective ligation strategies are a key success factor for chemical biology research. Ligation techniques open pathways to fully synthetic large peptides and even proteins.
Traceless Staudinger Ligation
The reaction between an azide and a phosphine forming an aza-ylide was discovered almost a century ago by Nobel Prize laureate Herrmann Staudinger.
Related Content
Professor Ron Raines works with Sigma-Aldrich on the development of reagents and tools for chemical biology such as the traceless Staudinger ligation reagent (670359). DTBA (774405), a superior biological reducing reagent to DTT, is another technology to come out of the Raines lab.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service