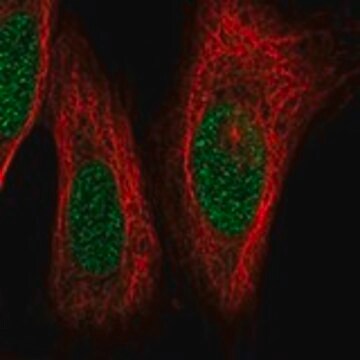
SAB4501395
Anti-Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase, N-Terminal antibody produced in rabbit
affinity isolated antibody
Synonyme(s) :
ACAC, ACACA, ACC-α, ACCA, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
rabbit
Niveau de qualité
Conjugué
unconjugated
Forme d'anticorps
affinity isolated antibody
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
polyclonal
Forme
buffered aqueous solution
Poids mol.
antigen 265 kDa
Espèces réactives
mouse, rat, human
Concentration
~1 mg/mL
Technique(s)
ELISA: 1:5000
immunohistochemistry: 1:50-1:100
western blot: 1:500-1:1000
Numéro d'accès NCBI
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Température de stockage
−20°C
Modification post-traductionnelle de la cible
unmodified
Informations sur le gène
human ... ACACA(31)
Description générale
Immunogène
Immunogen Range: 46-95
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Caractéristiques et avantages
Forme physique
Clause de non-responsabilité
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
nwg
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Articles
Information on fatty acid synthesis and metabolism in cancer cells. Learn how proliferatively active cells require fatty acids for functions such as membrane generation, protein modification, and bioenergetic requirements. These fatty acids are derived either from dietary sources or are synthesized by the cell.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique