I5771
Interleukin-6 Receptor Soluble Fragment human
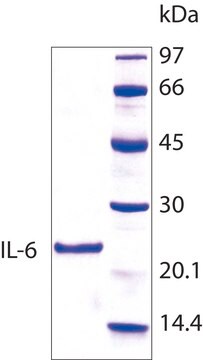
recombinant, expressed in Sf21 cells, ≥97% (SDS-PAGE), lyophilized powder
Synonyme(s) :
IL-6 sR
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Produit recombinant
expressed in Sf21 cells
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
≥97% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
lyophilized powder
Impuretés
endotoxin, tested
Température de stockage
−20°C
Description générale
Interleukin-6 is a pleotropic cytokine involved in hematopoiesis, inflammation and immune response. IL-6 is secreted by macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells, in response to TNF-α, PGDF and IL-1. The signaling by IL-6 is mediated by heterodimeric receptor, IL-6R, comprising of IL-6Rα (soluble factor) and gp130 (sometimes called IL-6Rβ). Gp130 is crucial component for downstream signal transduction. In response to IL-6, gp130 activates kinases of JAK family, STATs, MAPK and Ras proteins. IL-6R-mediated signaling is essential for normal development of T and B cells and has been implicated in many diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn disease, sepsis, fever, systemic lupus erythematosus, osteoporosis and insulin resistance
Interleukin-6 Receptor soluble fragment specifically binds and inhibits the activity of human IL-6 in free form or when bound to cell surface receptors.
Interleukin-6 Receptor soluble fragment specifically binds and inhibits the activity of human IL-6 in free form or when bound to cell surface receptors.
Application
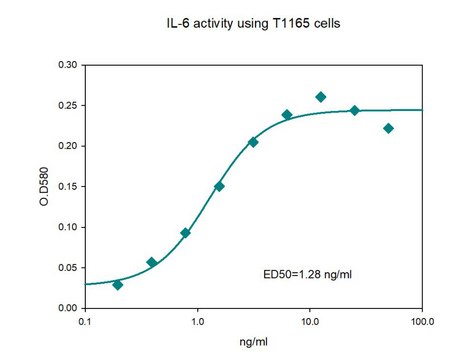
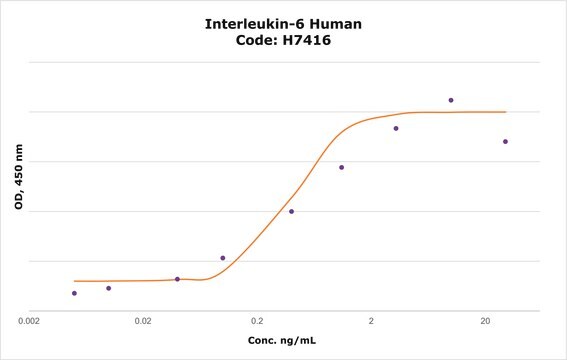
Interleukin-6 Receptor soluble fragment elicits a 50% increase in IL-6 activity in cell based assay at a concentration (EC50) of 1-10 ng/ml.
Forme physique
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in phosphate buffered saline containing 1.25 mg bovine serum albumin.
Remarque sur l'analyse
The receptor mediated activity of human IL-6 receptor soluble fragment is measured by its ability to increase the IL-6 inhibition of M1 cells.
Clause de non-responsabilité
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
David S Hong et al.
Cancer, 110(9), 1911-1928 (2007-09-13)
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) plays a major role in the response to injury or infection and is involved in the immune response, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. Its deregulation impacts numerous disease states, including many types of cancer. Consequently, modulating IL-6 may be an
Interleukin-6-type cytokines.
P B Sehgal et al.
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 762, 1-14 (1995-07-21)
Stefan Rose-John et al.
Journal of leukocyte biology, 80(2), 227-236 (2006-05-19)
Cytokine receptors, which exist in membrane-bound and soluble forms, bind their ligands with comparable affinity. Although most soluble receptors are antagonists and compete with their membrane-associated counterparts for the ligands, certain soluble receptors are agonists. In these cases, complexes of
Oliver Dienz et al.
Clinical immunology (Orlando, Fla.), 130(1), 27-33 (2008-10-11)
Cytokines have long been known to profoundly influence the adaptive immune response by determining CD4 T cell differentiation. Although IL-6 has been initially characterized as a B cell growth factor and inducer of antibody production research from our lab and
T van der Poll et al.
Infectious disease clinics of North America, 13(2), 413-426 (1999-05-26)
Clinical trials with anti-inflammatory agents in patients with sepsis are based on the assumption that excessive proinflammatory activity of the cytokine network negatively influences the outcome of severe bacterial infections. The failure of these trials to show clinical benefit, in
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique