C1740
Complement component C1q from human serum
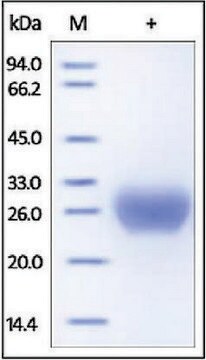
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonyme(s) :
C1q from human serum
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
human
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
liquid
Technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
Conditions d'expédition
dry ice
Température de stockage
−70°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
C1q, together with C1r and C1s, in the ratio of 1:2:2, form the C1 complex which is the first component of the classical complement pathway. C1q is composed of 18 polypeptide chains (six A, six B, six C) (MW 460 kDa). All contain an 81-aa collagen-like region composed of (Gly-Xaa-Yaa) repeating sequences close to the N-terminus. Three chains (A1B1C1) form a triple helix with the C-terminus forming the globular heads which may be structurally and functionally distinct domains.
Application
Complement component C1q is an important regulator factor for platelet activation. This has been a topic for research, as platelet-leukocyte aggregates play an important role in inflammatory conditions such as coronary heart disease. In particular, C1q has been shown to inhibit collagen induced aggregation and enhance production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
C1q deficiency, either because of rare homozygous genetic defect, or transcriptional/translational defects, is almost certainly a cause of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The three C1q subunits are expressed through a novel mechanism of transcriptional synchronization.
Forme physique
Supplied as a solution in 10 mM HEPES, 300 mM NaCl, pH 7.2
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Consol Farrera et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 191(5), 2647-2656 (2013-08-02)
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) facilitate the extracellular killing of pathogens. However, in recent years, excessive NET formation has been implicated in several pathological conditions. Indeed, NETs that are not removed from tissues or from the circulation might serve to trigger
Allison R Bialas et al.
Nature neuroscience, 16(12), 1773-1782 (2013-10-29)
Immune molecules, including complement proteins C1q and C3, have emerged as critical mediators of synaptic refinement and plasticity. Complement localizes to synapses and refines the developing visual system through C3-dependent microglial phagocytosis of synapses. Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) express C1q
Andrew D Greenhalgh et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 34(18), 6316-6322 (2014-05-03)
Macrophages in the injured spinal cord arise from resident microglia and infiltrating, peripherally derived monocytes. It is still not clear if macrophages derived from these two populations differ in their roles after CNS injury. The aims of this study are
Eduardo Sosoniuk et al.
Molecular immunology, 60(1), 80-85 (2014-04-29)
Trypanosoma cruzi, the agent of Chagas' disease, the sixth neglected tropical disease worldwide, infects 10-12 million people in Latin America. Differently from T. cruzi epimastigotes, trypomastigotes are complement-resistant and infective. CRPs, T-DAF, sialic acid and lipases explain at least part
Maria Cecilia S Freitas et al.
Transplantation, 95(9), 1113-1119 (2013-03-22)
Anti-HLA-DQ antibodies are the predominant HLA class II donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) after transplantation. Recently, de novo DQ DSA has been associated with worse allograft outcomes. The aim of this study was to determine the further complement-binding characteristics of the most
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique