53747
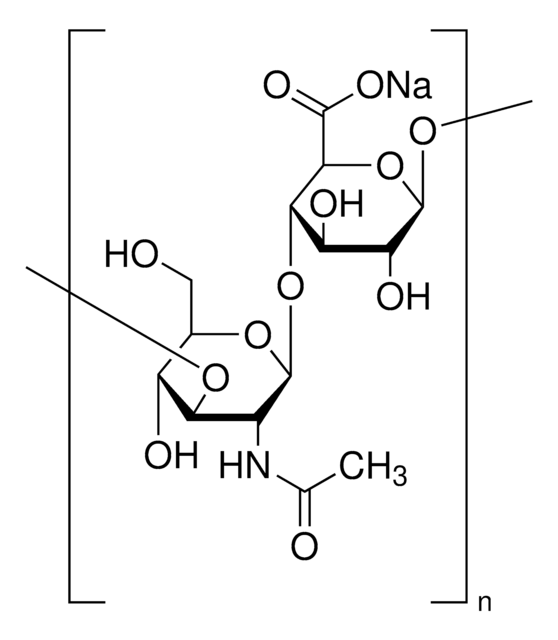
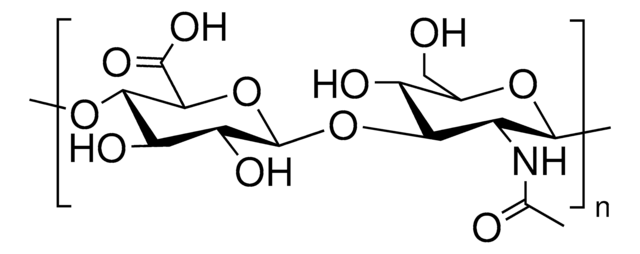
Hyaluronic acid sodium salt from Streptococcus equi
bacterial glycosaminoglycan polysaccharide
Synonyme(s) :
Poly(β-glucuronic acid-[1→3]-β-N-acetylglucosamine-[1→4]), alternating
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
(Streptococcus equi)
Niveau de qualité
Forme
powder or crystals
Poids mol.
~1.5-1.8 x 10E6 Da
Impuretés
≤1% protein
Couleur
white
Solubilité
H2O: 5 mg/mL, clear, colorless
Température de stockage
−20°C
Chaîne SMILES
[Na+].CC(=O)N[C@@H]1C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)O[C@@H]2C([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C28H44N2O23.Na/c1-5(33)29-9-18(11(35)7(3-31)47-25(9)46)49-28-17(41)15(39)20(22(53-28)24(44)45)51-26-10(30-6(2)34)19(12(36)8(4-32)48-26)50-27-16(40)13(37)14(38)21(52-27)23(42)43;/h7-22,25-28,31-32,35-41,46H,3-4H2,1-2H3,(H,29,33)(H,30,34)(H,42,43)(H,44,45);/q;+1/t7-,8-,9-,10-,11-,12-,13+,14+,15-,16-,17-,18-,19-,20+,21+,22+,25-,26+,27-,28-;/m1./s1
Clé InChI
YWIVKILSMZOHHF-QJZPQSOGSA-N
Description générale
Application
- with methacrylic anhydride for synthesizing cross-linkable methacrylated HA hydrogel (Coll-MeHA)
- in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) to replace the PBS bath to vary the lubricant composition
- in the preparation of lubricant to study its effects on the boundary lubrication of human osteoarthritis (OA) cartilage
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Autres remarques
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Glycosaminoglycans are large linear polysaccharides constructed of repeating disaccharide units.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique