DIUTP-RO
Roche
Digoxigénine-11-dUTP, labile en milieu alcalin
=85% (HPLC), solution, pkg of 25 μL (11573152910 [1 mM]), pkg of 125 μL (11573179910 [1 mM]]])
Synonyme(s) :
Digoxigenin-11-dUTP, alkali-labile, digoxigenin
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Code UNSPSC :
41105500
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
85% (HPLC)
Forme
solution
Conditionnement
pkg of 125 μL (11573179910 [1 mM]]])
pkg of 25 μL (11573152910 [1 mM])
Fabricant/nom de marque
Roche
Température de stockage
−20°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
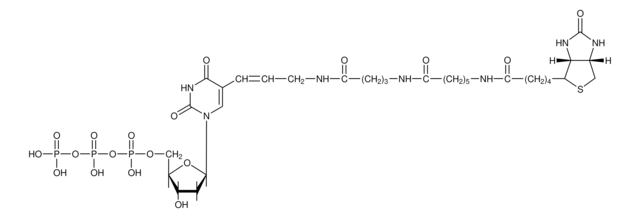
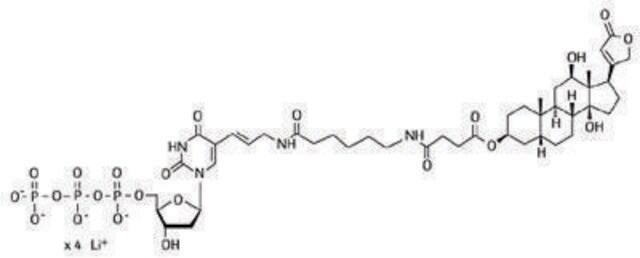
Digoxigenin (DIG)-11-deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP), alkali-labile is provided as in 1 mM tetralithium salt, solution. In which DIG is bound to dUTP via an alkali-sensitive ester linkage.
Application
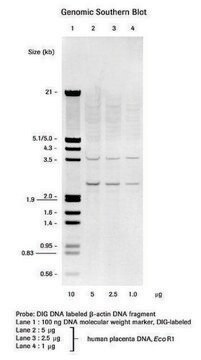
Digoxigenin-11-dUTP, alkali-labile can be used for non-radioactive DNA labeling e.g. random primed or nick translation. It can also be used for labeling probes which are preferred in hybridization experiments where stripping and reprobing of the membrane is intended.
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Digoxigenin (DIG)-11-deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) replaces deoxythymidine triphophate (dTTP) in the random-primed DNA labeling reaction or in nick translation in a ratio of 35% DIG-11-dUTP and 65% dTTP. It is ideal as a substrate for DNA polymerase, Taq DNA polymerase, terminal transferase and reverse transcriptase.
Autres remarques
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
When this nucleotide is subjected to 0.1 - 0.5 NaOH at +15 to +25°C, the DIG moiety will be removed. It is therefore ideal for use in DIG-labeled probes that can be removed by alkali denaturation (e.g ., in stripping and reprobing of blots). However, if you intend to make a DIG-labeled DNA that will survive alkaline treatment, do not use this alkali-labile preparation. Instead, use the alkali-stable form of DIG-11-dUTP.
When this nucleotide is subjected to 0.1 - 0.5 NaOH at +15 to +25°C, the DIG moiety will be removed. It is therefore ideal for use in DIG-labeled probes that can be removed by alkali denaturation (e.g ., in stripping and reprobing of blots). However, if you intend to make a DIG-labeled DNA that will survive alkaline treatment, do not use this alkali-labile preparation. Instead, use the alkali-stable form of DIG-11-dUTP.
Souvent commandé avec ce produit
Réf. du produit
Description
Tarif
Code de la classe de stockage
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
nwg
Point d'éclair (°F)
does not flash
Point d'éclair (°C)
does not flash
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
James E Dombrowski et al.
BMC research notes, 4, 46-46 (2011-03-08)
Choke, caused by the endophytic fungus Epichloë typhina, is an important disease affecting orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.) seed production in the Willamette Valley. Little is known concerning the conditions necessary for successful infection of orchardgrass by E. typhina. Detection of
Interstitial telomeric sequence blocks in constitutive pericentromeric heterochromatin from Pyrgomorpha conica (Orthoptera) are enriched in constitutive alkali-labile sites
Lopez-Fernandez, Carmen, et al
Mutation Research. Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 599 (1), 36-44 (2006)
Araceli Nora García et al.
BMC plant biology, 14, 248-248 (2014-09-18)
The production of antimicrobial peptides is a common defense strategy of living cells against a wide range of pathogens. Plant snakin peptides inhibit bacterial and fungal growth at extremely low concentrations. However, little is known of their molecular and ecological
Sara Bembich et al.
Nucleic acids research, 42(5), 3362-3371 (2013-12-27)
TDP-43 is a nuclear protein involved in many aspects of RNA metabolism. To ensure cellular viability, its expression levels within cells must be tightly regulated. We have previously demonstrated that TDP-43 autoregulation occurs through the activation of a normally silent
Eric Röttinger et al.
PLoS genetics, 8(12), e1003164-e1003164 (2013-01-10)
Understanding the functional relationship between intracellular factors and extracellular signals is required for reconstructing gene regulatory networks (GRN) involved in complex biological processes. One of the best-studied bilaterian GRNs describes endomesoderm specification and predicts that both mesoderm and endoderm arose
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique