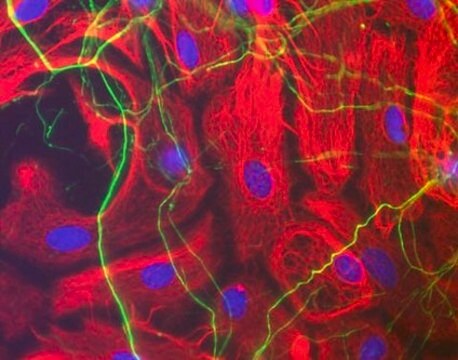
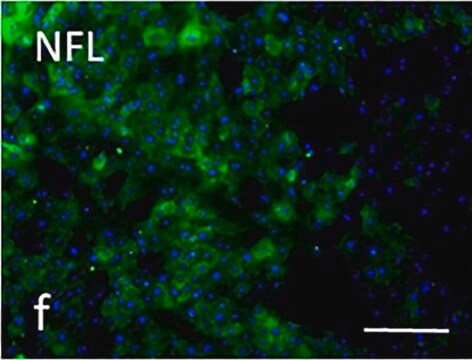
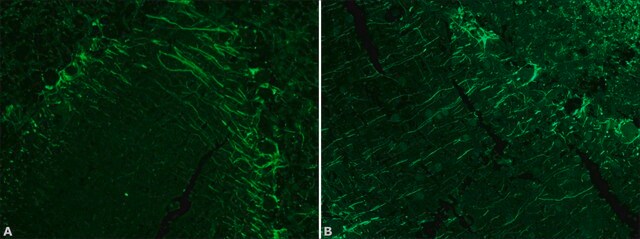
NE1022
PhosphoDetect Anti-Neurofilament H Mouse mAb (SMI-31)
liquid, clone SMI-31, Calbiochem®
Synonyme(s) :
Anti-neurofilament antibody
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
mouse
Niveau de qualité
Forme d'anticorps
purified antibody
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
SMI-31, monoclonal
Forme
liquid
Contient
≤0.1% sodium azide as preservative
Espèces réactives
chicken, Xenopus
Réactivité de l'espèce (prédite par homologie)
mammals
Fabricant/nom de marque
Calbiochem®
Conditions de stockage
OK to freeze
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
Isotype
IgG1
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Modification post-traductionnelle de la cible
unmodified
Informations sur le gène
human ... NEFH(4744)
Description générale
Immunogène
Application
ELISA (1:1000)
Frozen Sections (1:1000, see comments)
Immunoblotting (1:1000)
Immunocytochemistry (1:1000, see comments)
Paraffin Sections (1:1000, heat pre-treatment required, see comments)
Immunoprecipitation (see comments)
Avertissement
Forme physique
Autres remarques
Yang, C.C., et al. 1998. Brain121, 1089.
Giasson, B.I and Mushynski, W.E. 1996. J. Biol. Chem.271, 30404.
Mirabella, M., et al. 1996. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol.55, 774.
Xiao, J. and Monteiro, M.J. 1994. J. Neurosci.14, 1820.
Informations légales
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Code de la classe de stockage
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
nwg
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique