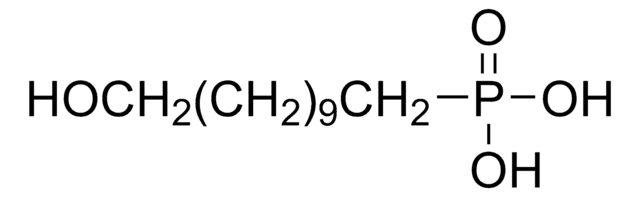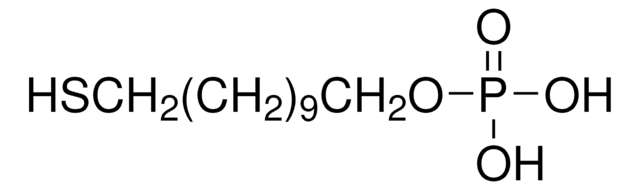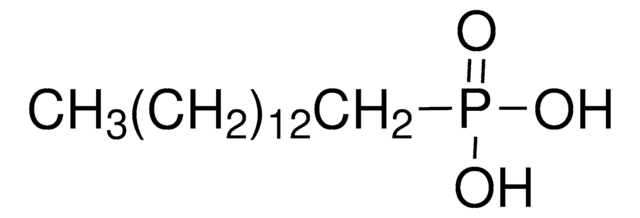685801
16-Phosphonohexadecanoic acid
97%
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Pureté
97%
Forme
solid
Pf
129-133 °C
Chaîne SMILES
OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCP(O)(O)=O
InChI
1S/C16H33O5P/c17-16(18)14-12-10-8-6-4-2-1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-22(19,20)21/h1-15H2,(H,17,18)(H2,19,20,21)
Clé InChI
JVXYHUCXFLBBGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Description générale
Application
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
There is widespread demand for thin, lightweight, and flexible electronic devices such as displays, sensors, actuators, and radio-frequency identification tags (RFIDs). Flexibility is necessary for scalability, portability, and mechanical robustness.
Inorganic nanomaterials are tunable by size, shape, structure, and/or composition. Advances in the synthesis of well-defined nanomaterials have enabled control over their unique optical, electronic, and chemical properties stimulating tremendous interest across a wide range of disciplines. This article illuminates some of the recent research advances of inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) in optoelectronics applications.
Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) have attracted enormous interest for a wide variety of applications in micro- and nano-technology. In this article, we compare the benefits of three different classes of SAM systems (alkylthiolates on gold.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique