436224
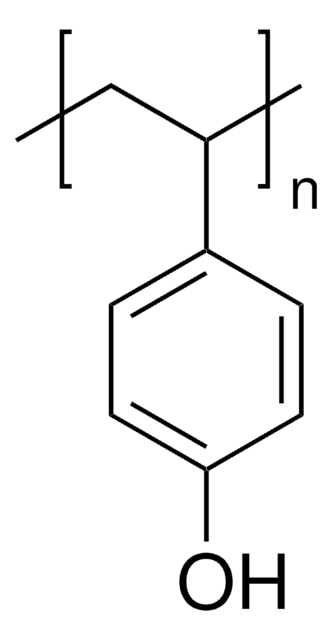
Poly(4-vinylphenol)
average Mw ~25,000
Synonyme(s) :
PVP
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Description
intrinsic viscosity parameters α=0.50, k=9.71 × 10-4 dL/g 25°C, in THF
Forme
powder
Poids mol.
average Mw ~25,000
Caractéristiques du produit alternatif plus écologique
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Viscosité intrinsèque
(α=0.50, k=9.71 × 10-4)
Pf
360 °C (dec.)
Température de transition
Tg 130-185 °C
Solubilité
alcohols, ethers, ketones and esters: soluble
aromatics, petroleum ethers and chlorinated hydrocarbons: insoluble
Densité
1.16 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Autre catégorie plus écologique
, Enabling
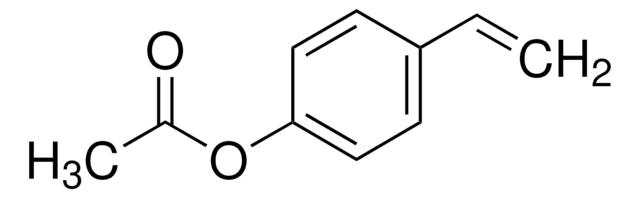
Chaîne SMILES
Oc1ccc(C=C)cc1
InChI
1S/C8H10O/c1-2-7-3-5-8(9)6-4-7/h3-6,9H,2H2,1H3
Clé InChI
HXDOZKJGKXYMEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique