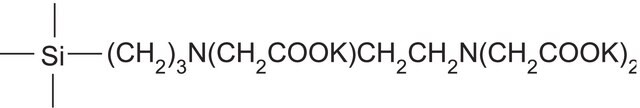52737-U
Discovery® DSC-WCX SPE Tube
bed wt. 50 mg, volume 1 mL, pk of 108
About This Item
Recommended Products
material
polypropylene tube
Quality Level
product line
Discovery®
composition
bed wt., 50 mg
packaging
pk of 108
technique(s)
solid phase extraction (SPE): suitable
surface area
480 m2/g
volume
1 mL
matrix
Silica gel base material (irregularly shaped, acid washed)
matrix active group
carboxypropyl bonding
particle size
50 μm
pore size
0.9 mL/g pore volume
70 Å pore diameter
capacity
0.15 meq/g total capacity
application(s)
food and beverages
separation technique
ion exchange
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Sample Matrix Compatibility: Organic or aqueous solutions
- A polymerically bonded, ethylenediamine triacetic acid phase with a pKa of 4.8
- Counter ion is Na+
- Ion exchange capacity is ∼ 0.15 meq/g
- Carries a negative charge at pH 6.8 or above
- A pH of 2.8 or below neutralizes this phase for easier elution of strong cationic analytes that are neutralized only at extreme basic conditions
- Typically used when dealing with very strong cationic (high pKa) compounds that may be irreversibly retained on strong cation exchangers
Legal Information
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
>464.0 °F
Flash Point(C)
> 240 °C
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
SPE retention mechanism in this case is based on the electrostatic attraction of charged functional groups of the analyte(s) to oppositely charged functional groups on the sorbent.
Protocols
Retention occurs through polar interaction between the sorbent and analytes. Typical sample matrices that can be employed in normal-phase SPE include hydrocarbon or fatty oils diluted in a solvent like hexane, isooctane, chlorinated solvent, THF, diethyl ether, or ethyl acetate.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service