SAB4700630
Monoclonal Anti-5-bromodeoxyuridine antibody produced in mouse
clone MoBu-1, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-BrdU
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.41
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
MoBu-1, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
concentration
1 mg/mL
technique(s)
flow cytometry: suitable
isotype
IgG1
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
The antibody MoBu-1 reacts specifically with BrdU incorporated into DNA during S-phase of a cell cycle. The antibody MoBu-1 is also useful for detecting proliferating cells by flow cytometry or immunofluorescence staining. It reacts also specifically with 5-bromouridine (BrU).
Immunogen
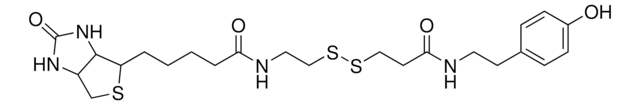
5-bromodeoxyuridine conjugated with hemocyanine
Application
Monoclonal Anti-5-bromodeoxyuridine antibody produced in mouse has been used in Immunocytochemistry. The reagent is designed for Flow Cytometry analysis. Suggested working dilution for Flow Cytometry is 1-2 μg/mL of sample. Indicated dilution is recommended starting point for use of this product. Working concentrations should be determined by the investigator.
Biochem/physiol Actions
5-Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) is an analogue of thymidine, used to measure DNA synthesis immunochemically in living cells. BrdU along with cAMP and butyrate plays a vital role in the cellular differentiation in several mammalian cell types. It also inhibits cell growth in mammalian and yeast cells by modulating the expression of particular genes involved in cell division. In the absence of DNA synthesis, brdu promotes mouse neuroblastoma C1300 cell differentiation into cells that morphologically are similar to mature neurons. BrdU activates cell senescence-like phenomenon in mammalian cells.
Features and Benefits
Evaluate our antibodies with complete peace of mind. If the antibody does not perform in your application, we will issue a full credit or replacement antibody. Learn more.
Physical form
Solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, with 15 mM sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
D Stanek et al.
European journal of cell biology, 79(3), 202-207 (2000-04-25)
The available data concerning the subnucleolar localisation of the individual steps of precursor-ribosomal RNA (pre-rRNA) processing are ambiguous. According to in situ hybridisation studies, the late steps of pre-rRNA processing have been located into the granular component of the nucleolus
Alessio Ligabue et al.
PloS one, 7(10), e47318-e47318 (2012-10-12)
5-fluorouracil, a commonly used chemotherapeutic agent, up-regulates expression of human thymidylate synthase (hTS). Several different regulatory mechanisms have been proposed to mediate this up-regulation in distinct cell lines, but their specific contributions in a single cell line have not been
Overexpression of HAM1 gene detoxifies 5-bromodeoxyuridine in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Takayama S, et al.
Current Genetics, 52(5-6), 203-211 (2007)
AT-hook proteins stimulate induction of senescence markers triggered by 5-bromodeoxyuridine in mammalian cells.
Satou W, et al.
Experimental Gerontology, 39(2), 173-179 (2004)
5-bromodeoxyuridine-induced differentiation of a neuroblastoma.
Schubert D and Jacob F.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 67(1), 247-254 (1970)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service