MBD0039
Proteus FISH probe - ATTO488
Probe for fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH),20 μM in water
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(6)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.55
Recommended Products
Quality Level
technique(s)
FISH: suitable
fluorescence
λex 504 nm; λem 521 nm (ATTO488)
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization technique (FISH) is based on the hybridization of fluorescent labeled oligonucleotide probe to a specific complementary DNA or RNA sequence in whole and intact cells.1 Microbial FISH allows the visualization, identification and isolation of bacteria due to recognition of ribosomal RNA also in unculturable samples.2
FISH technique can serve as a powerful tool in the microbiome research field by allowing the observation of native microbial populations in diverse microbiome environments, such as samples from human origin (blood3 and tissue4), microbial ecology (solid biofilms5 and aquatic systems6) and plants7. It is strongly recommended to include positive and negative controls in FISH assays to ensure specific binding of the probe of interest and appropriate protocol conditions. We offer positive (MBD0032/33) and negative (MBD0034/35) control probes, that accompany the specific probe of interest.
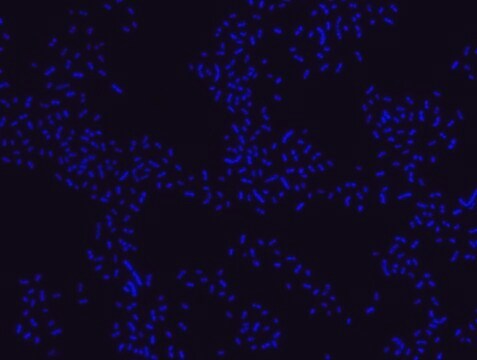
Proteus probe specifically recognizes Proteus species (see images of Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis). Moreover, it was shown that this probe recognizes Proteus penneri and Proteus hauseri.16
P. mirabilis and P. vulgaris are gram negative facultative anaerobic rod-shaped bacteria. Bacteria of the genus Proteus (Proteus spp.) of the family Enterobacteriaceae are opportunistic human pathogens, that often reside in the human intestine, and are responsible for wound and burn infections as well as skin, eye, ear, nose, throat, urinary tract, and gastrointestinal infections and bacteremias.8,9 Proteus genus that includes P. mirabilis, P. vulgaris, Proteus penneri and Proteus hauseri, are widespread in the environment and often serve as an indicator for soil or water fecal pollution.9
P. mirabilis causes up to 90% of all Proteus spp. infections and is more frequently associated with urinary tract infections then P. vulgaris.9
Proteus spp. have various virulence factors such as, fimbriae, flagella, enzymes (urease, proteases, and amino acid deaminases), and toxins (hemolysins and endotoxin).10
The most common infection involving P.mirabilis occurs when the bacteria, which is a member of the natural intestinal flora, moves to the urethra and urinary bladder causing urinary tract infection. The outer-membrane lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is considered an important virulence factor of Proteus.10 The immunological response against P.mirabilis LPS might play a role in rheumatoid arthritis.11 A possible correlation between the abundance of
P. mirabilis in the intestine and obesity was suggested recently.12
P. vulgaris inhabits the intestinal tract of humans and animals and can be found in soil, water and feces.8 Moreover, it was also observed in fecal samples of healthy individuals.13
P. mirabilis has developed resistance to various classes of antibiotics, such as β-lactams aminoglycosides and tetracyclines.14 However, P.mirabilis strains are generally more
susceptible to antimicrobials than are P. vulgaris, P. penneri, and P. hauseri.15
FISH technique was successfully used for clinical detection of Proteus spp. in artificial urine medium and urine samples from patients with UTIs. The probe was able to detect 11 strains of P.mirabilis, 6 strains of P.vulgaris, 2 strains of P. penneri and one strain of P.hauseri.16 The probe can also be used to detect P.mirabilis and P.vulgaris pure culture (as described in the figure legends). FISH can also be implicated to detect Proteus spp. in colon sections embedded in paraffin.17,18 Moreover, FISH can be implicated to identify Proteus spp. in the gut of the medicinal leech.19
FISH technique can serve as a powerful tool in the microbiome research field by allowing the observation of native microbial populations in diverse microbiome environments, such as samples from human origin (blood3 and tissue4), microbial ecology (solid biofilms5 and aquatic systems6) and plants7. It is strongly recommended to include positive and negative controls in FISH assays to ensure specific binding of the probe of interest and appropriate protocol conditions. We offer positive (MBD0032/33) and negative (MBD0034/35) control probes, that accompany the specific probe of interest.
Proteus probe specifically recognizes Proteus species (see images of Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis). Moreover, it was shown that this probe recognizes Proteus penneri and Proteus hauseri.16
P. mirabilis and P. vulgaris are gram negative facultative anaerobic rod-shaped bacteria. Bacteria of the genus Proteus (Proteus spp.) of the family Enterobacteriaceae are opportunistic human pathogens, that often reside in the human intestine, and are responsible for wound and burn infections as well as skin, eye, ear, nose, throat, urinary tract, and gastrointestinal infections and bacteremias.8,9 Proteus genus that includes P. mirabilis, P. vulgaris, Proteus penneri and Proteus hauseri, are widespread in the environment and often serve as an indicator for soil or water fecal pollution.9
P. mirabilis causes up to 90% of all Proteus spp. infections and is more frequently associated with urinary tract infections then P. vulgaris.9
Proteus spp. have various virulence factors such as, fimbriae, flagella, enzymes (urease, proteases, and amino acid deaminases), and toxins (hemolysins and endotoxin).10
The most common infection involving P.mirabilis occurs when the bacteria, which is a member of the natural intestinal flora, moves to the urethra and urinary bladder causing urinary tract infection. The outer-membrane lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is considered an important virulence factor of Proteus.10 The immunological response against P.mirabilis LPS might play a role in rheumatoid arthritis.11 A possible correlation between the abundance of
P. mirabilis in the intestine and obesity was suggested recently.12
P. vulgaris inhabits the intestinal tract of humans and animals and can be found in soil, water and feces.8 Moreover, it was also observed in fecal samples of healthy individuals.13
P. mirabilis has developed resistance to various classes of antibiotics, such as β-lactams aminoglycosides and tetracyclines.14 However, P.mirabilis strains are generally more
susceptible to antimicrobials than are P. vulgaris, P. penneri, and P. hauseri.15
FISH technique was successfully used for clinical detection of Proteus spp. in artificial urine medium and urine samples from patients with UTIs. The probe was able to detect 11 strains of P.mirabilis, 6 strains of P.vulgaris, 2 strains of P. penneri and one strain of P.hauseri.16 The probe can also be used to detect P.mirabilis and P.vulgaris pure culture (as described in the figure legends). FISH can also be implicated to detect Proteus spp. in colon sections embedded in paraffin.17,18 Moreover, FISH can be implicated to identify Proteus spp. in the gut of the medicinal leech.19
Application
Probe for fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), recognizes Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis cells.
Features and Benefits
- Visualize, identify and isolate Proteus spp. cells.
- Observe native Proteus spp. cell populations in diverse microbiome environments.
- Specific, sensitive and robust identification of Proteus spp. in bacterial mixed population.
- Specific, sensitive and robust identification even when Proteus spp. are in low abundance in the sample.
- FISH can complete PCR based detection methods by avoiding contaminant bacteria detection.
- Provides information on Proteus spp. morphology and allows to study biofilm architecture.
- Identify Proteus spp. in clinical samples such as, urine samples and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples.
- The ability to detect Proteus spp. in its natural habitat is an essential tool for studying host-microbiome interaction.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
C M O'Hara et al.
Clinical microbiology reviews, 13(4), 534-546 (2000-10-12)
This review presents the current taxonomy of the genera Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella, along with the current methods for the identification of each species within the three genera, incorporating both conventional biochemical and commercial methods. While all of these organisms
D C Morrison et al.
Annual review of medicine, 38, 417-432 (1987-01-01)
In this chapter, current concepts about the mechanisms of action of endotoxin are reviewed. Particular attention is focused upon endotoxin-induced production of soluble mediators from macrophages and mononuclear cells and on the potential contribution of these mediators to endotoxin shock.
Jiming Jiang
Chromosome research : an international journal on the molecular, supramolecular and evolutionary aspects of chromosome biology, 27(3), 153-165 (2019-03-11)
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was developed more than 30 years ago and has been the most paradigm-changing technique in cytogenetic research. FISH has been used to answer questions related to structure, mutation, and evolution of not only individual chromosomes but
Michael Wagner et al.
Current opinion in microbiology, 6(3), 302-309 (2003-07-02)
Fluorescence in situ hybridisation with rRNA-targeted nucleic acid probes can be used to directly identify microorganisms within complex samples in a few hours and therefore has widespread application in environmental and medical microbiology. The past year has seen significant methodological
Virginie Lecomte et al.
PloS one, 10(5), e0126931-e0126931 (2015-05-21)
The gut microbiota is emerging as a new factor in the development of obesity. Many studies have described changes in microbiota composition in response to obesity and high fat diet (HFD) at the phylum level. In this study we used
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service