C6624
Carbonic Anhydrase II human
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
CA-II, CA2, Carbonic Anhydrase 2
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Quality Level
form
buffered aqueous solution
specific activity
≥5,000 units/mg protein
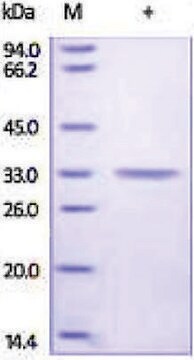
mol wt
large subunit 17-22 kDa
small subunit 10-12 kDa
concentration
800-1000 μg/mL
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... CA2(760)
Application
Human carbonic anhydrase II has been used in a study to assess quantitative imaging of mitochondrial and cytosolic free zinc levels in an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion. Human carbonic anhydrase II has also been used in a study to investigate a new scrubber concept for catalytic CO2 hydration.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Carbonic anhydrase is a zinc metalloenzyme that catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to carbonic acid. It is involved in vital physiological and pathological processes such as pH and CO2 homeostasis, transport of bicarbonate and CO2, biosynthetic reactions, bone resorption, calcification, and tumorigenicity. It is required for renal acidification. Its absence can lead to osteoporosis, renal tubular acidosis, and cerebral calcification. Therefore, this enzyme is an important target for inhibitors with clinical applications in glaucoma, epilepsy and Parkinson′s disease. In addition, it is being explored as a potential target for obesity and cancer. CAII has a molecular mass of approximately 30 kDa and is primarily present in type II pneumocytes. Due to this unique location it has been speculated that CAII is involved in pulmonary functions such as regulation of fluid secretion and facilitation of CO2 elimation. Sulfonamides, sulfamates and sulfamides are potent inhibitors of CA.
Unit Definition
One Wilbur-Anderson (W-A) unit will cause the pH of a 0.02 M Trizma buffer to drop from 8.3 to 6.3 per min at 0 °C. (One W-A unit is essentially equivalent to one Roughton-Booth unit.)
Physical form
Supplied as a solution in 20 mM Tris, pH 7.5, with 150 mM NaCl.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Samira Ranjbar et al.
International journal of biological macromolecules, 50(4), 910-917 (2012-02-22)
This study reports the interaction between furosemide and human carbonic anhydrase II (hCA II) using fluorescence, UV-vis and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Fluorescence data indicated that furosemide quenches the intrinsic fluorescence of the enzyme via a static mechanism and hydrogen
Bryan J McCranor et al.
Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes, 44(2), 253-263 (2012-03-21)
The role of zinc ion in cytotoxicity following ischemic stroke, prolonged status epilepticus, and traumatic brain injury remains controversial, but likely is the result of mitochondrial dysfunction. We describe an excitation ratiometric fluorescence biosensor based on human carbonic anhydrase II
New scrubber concept for catalytic CO2 hydration by immobilized carbonic anhydrase II and in-situ inhibitor removal in three-phase monolith slurry reactor
Iliuta, I. and F. Larachi
Separation and Purification Technology, 86, 199-214 (2012)
John J Desmarais et al.
Nature microbiology, 4(12), 2204-2215 (2019-08-14)
Bacterial autotrophs often rely on CO2 concentrating mechanisms (CCMs) to assimilate carbon. Although many CCM proteins have been identified, a systematic screen of the components of CCMs is lacking. Here, we performed a genome-wide barcoded transposon screen to identify essential
Screening and docking studies of natural phenolic inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase II
Huang HQ, et al.
Science in China. Series B, Chemistry, Life Sciences & Earth Sciences, 52(3), 332-337 (2009)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service