S7705
TRAPeze™1X CHAPS Lysis Buffer
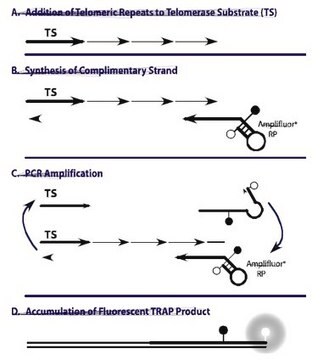
1X CHAPS Lysis Buffer is a component of the gel-and ELISA-based TRAPeze Telomerase Detection Kits & is used in the extraction step of the procedure.
Synonym(s):
CHAPS Lysis Buffer
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41116012
eCl@ss:
32160405
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
General description
1X CHAPS Lysis Buffer is a component of the gel- and ELISA-based TRAPeze Telomerase Detection Kits and is used in the extraction step of the procedure.
Used to supplement the TRAPEZE Kit assay when larger tissue samples necessitate additional 1X CHAPS Lysis Buffer for efficient cell lysis. It extends the capabilities of the kits by enabling the analysis of larger tissue samples.
Application
TRAPeze™1X CHAPS Lysis Buffer has been used:
- to extract total proteins from HEK293 cells in quantitative telomerase activity assay (Q-TRAP)
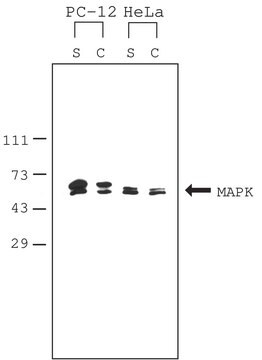
- to homogenize mouse atrial tissues for western blots analysis
- in telomerase expression analysis of cell lines to resuspend the cells to determine protein concentration
Storage and Stability
Store at 4°C.
Legal Information
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
TRAPEZE is a trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Yu-Feng Hu et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular basis of disease, 1867(5), 166088-166088 (2021-01-31)
Point mutation in alcohol dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2), ALDH2*2 results in decreased catalytic enzyme activity and has been found to be associated with different human pathologies. Whether ALDH2*2 would induce cardiac remodeling and increase the attack of atrial fibrillation (AF) remains
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service