335681
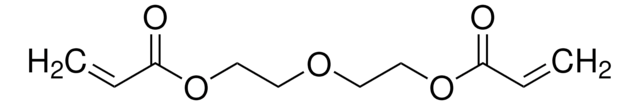
Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate
98%, cross-linking reagent polymerization reactions, methacrylate, 90-110 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
Synonym(s):
Polyethylene glycol, 1,2-Ethanediol dimethacrylate, Ethylene dimethacrylate
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, 98%, contains 90-110 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
vapor density
>1 (vs air)
Quality Level
vapor pressure
<0.1 mmHg ( 21.1 °C)
Assay
98%
form
liquid
contains
90-110 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
reaction suitability
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
refractive index
n20/D 1.454 (lit.)
bp
98-100 °C/5 mmHg (lit.)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- A terpolymer system, poly(acrylonitrile-co-Ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate-co-vinylbenzyl chloride), which is applicable as a sorbentin pharmaceuticals adsorption.
- PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) based hydrogel by free-radicalcopolymerization. These PVA polymer networks can be used as drug deliverysystems.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
219.2 °F - Pensky-Martens closed cup
Flash Point(C)
104 °C - Pensky-Martens closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service