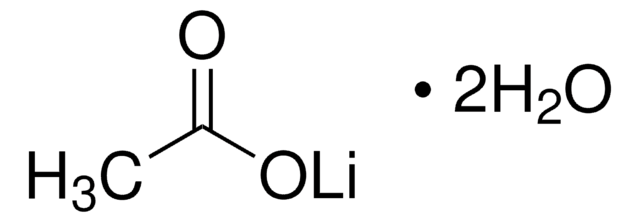
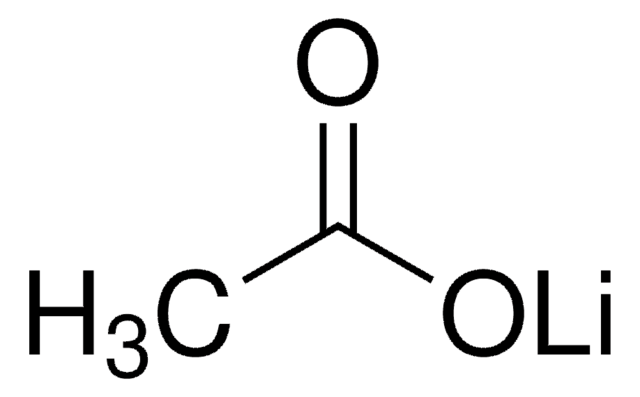
YEAST1
Yeast Transformation Kit
reagents for introducing plasmid DNA into yeast
Synonym(e):
lithium acetate yeast transformation
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
for molecular biology
Qualitätsniveau
Verwendung
kit sufficient for >100 standard transformations
Methode(n)
transformation: suitable
Versandbedingung
dry ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Verwandte Kategorien
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
- Easy and ready-to-use
- Requires as little as 10 ng of plasmid DNA
- Flexibility for any strain of yeast
- Sufficient for over 100 standard transformations
Komponenten
- Transformation Buffer; 100 ml; 100 mM lithium acetate, 10 mM Tris HCl, pH 7.6, and 1 mM EDTA
- Plate Buffer; 100 ml; 40% PEG, 100 mM lithium acetate, 10 mM Tris HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA
- Deoxyribonucleic acid from salmon teste, 10 mg/ml; 2 x 1 ml
- Control Yeast Plasmid DNA pRS316 carrying the ura gene; 10 μg
- Yeast Synthetic Drop-out Medium Supplement Without Uracil; 1 g
Prinzip
Ähnliches Produkt
Lagerklassenschlüssel
10 - Combustible liquids
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Transformation is the process by which exogenous DNA is introduced into a cell, resulting in a heritable change or genetic modification. This was first reported in Streptococcus pneumoniae by Griffith in 1928. Transforming principle of DNA was demonstrated by Avery et al. in 1944.
The development of genetic engineering and cloning has opened many possibilities of expression and isolation of heterologous proteins for research purposes. Considerable advances in technology have enabled expression and isolation of recombinant proteins in large scale.
Protokolle
The selection of plasmids in yeast is based on the use of auxotrophic mutant strains, which cannot grow without a specific medium component (an amino acid, purine, or pyrimidine)
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.