P5115
Polypep® Low Viscosity
histochemical stabilizer
Synonym(e):
Low Viscosity Polypeptide, Polypep Solution
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(3)
About This Item
UNSPSC-Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.83
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Form
powder
Allgemeine Beschreibung
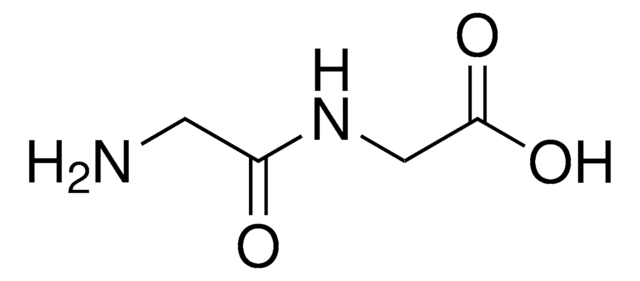
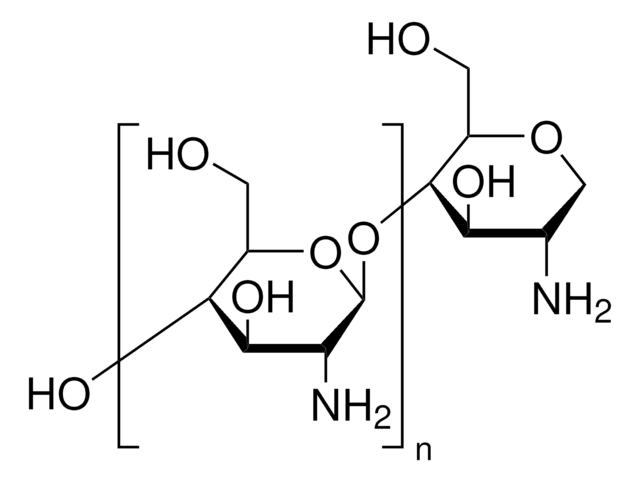
A proprietary protein digest that provides increased stablization of tissue sections in histochemical studies.
Anwendung
Polypep® Low Viscosity has been used as a component of substrate incubation medium to act as a section stabilizer. It has also been used for enzyme cytochemistry.
Rechtliche Hinweise
Polypep is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
A A Pitsillides et al.
Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research, 14(6), 980-987 (1999-06-03)
Bone's functional competence is established and maintained, at least partly, by mechanisms involving appropriate adaptation to mechanical loading. These appear to fail in chickens selectively bred either for maximum egg (Egg-type) or meat (Meat-type) production, which show high rates of
Lysosomal membrane stability in mussels.
Martinez GC, et al.
ICES Journal of Marine Science (2015)
Bivalve immunity: comparisons between the marine mussel (Mytilus edulis), the edible cockle (Cerastoderma edule) and the razor-shell (Ensis siliqua)
Wootton EC, et al.
Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 15(3), 195-210 (2003)
Simon C F Rawlinson et al.
Bone, 45(2), 357-366 (2009-05-05)
Bone strength is, in part, dependent on a mechanical input that regulates the (re)modelling of skeletal elements to an appropriate size and architecture to resist fracture during habitual use. The rate of longitudinal bone growth in juveniles can also affect
Maes Thomas et al.
Heliyon, 6(1), e03103-e03103 (2020-01-08)
Bivalve filter feeders, such as oysters, filter large volumes of water and are particularly exposed to microplastics (MP). Consequently, these animals digest and assimilate high levels of MP in their bodies that may likely impact their physiology, and potentially affect
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.