Alle Fotos(1)
Wichtige Dokumente
L7920
β-Lactamase Blend
recombinant, expressed in E. coli
Synonym(e):
Carbapenemase, Cephalosprinase
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Rekombinant
expressed in E. coli
Qualitätsniveau
Sterilität
γ-irradiated
Form
lyophilized powder
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
Allgemeine Beschreibung
No detectable growth in tryptone soy broth at 30-35 °C for 14 days
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
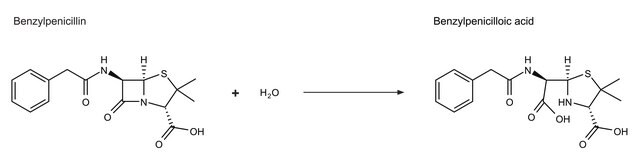
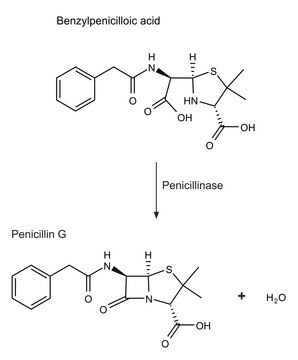
β-Lactamases exhibit high carbapenemase activity. β-lactamases can destroy the β-lactam ring. True carbapenemases has the ability to hydrolyse several β-lactam ring containing carbapenems like meropenem, doripenem, imipenem and ertapenem.
Komponenten
600-1500 IU beta-lactamase I per vial
60-150 IU beta-lactamase II per vial
60-150 IU beta-lactamase II per vial
Einheitendefinition
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole substrate per min (βI: benzylpenicillin; βII: cephalosporin C) in phosphate buffer, pH 7.0 at 25°C.
Physikalische Form
Lyophilized powder containing sodium chloride, potassium phosphate, dipotassium phosphate and sorbitol.
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Identification and screening of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae
Nordmann P, et al.
Clinical Microbiology and Infection : the Official Publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 18(5), 432-438 (2012)
Lisa M Miller et al.
ACS applied materials & interfaces, 11(36), 32599-32604 (2019-08-27)
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has been identified as a major threat to public health worldwide. To ensure appropriate use of existing antibiotics, rapid and reliable tests of AMR are necessary. One of the most common and clinically important forms of bacterial
Mechanisms and Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance
Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases (Fourth Edition), 1467-1478 (2017)
Matthew D Simmons et al.
Antibiotics (Basel, Switzerland), 9(10) (2020-10-03)
The misuse of antibiotics in health care has led to increasing levels of drug resistant infections (DRI's) occurring in the general population. Most technologies developed for the detection of DRI's typically focus on phenotyping or genotyping bacterial resistance rather than
Prevalence of faecal carriage of NDM-1-producing bacteria among patients with diarrhoea in Bangladesh.
Mohammad Aminul Islam et al.
Journal of medical microbiology, 63(Pt 4), 620-622 (2014-02-04)
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.