Wichtige Dokumente
E9906
Anti-EDEM2 (N-terminal) antibody produced in rabbit
~1.0 mg/mL, affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(e):
Anti-ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 2
About This Item
WB
western blot: 0.5-1 μg/mL using whole extracts of HEK-293T cells expressing recombinant human EDEM2
Empfohlene Produkte
Biologische Quelle
rabbit
Konjugat
unconjugated
Antikörperform
affinity isolated antibody
Antikörper-Produkttyp
primary antibodies
Klon
polyclonal
Form
buffered aqueous solution
Mol-Gew.
antigen ~70 kDa
Speziesreaktivität
human, rat (predicted), mouse
Konzentration
~1.0 mg/mL
Methode(n)
indirect immunofluorescence: 5-10 μg/mL using mouse 3T3 cells
western blot: 0.5-1 μg/mL using whole extracts of HEK-293T cells expressing recombinant human EDEM2
UniProt-Hinterlegungsnummer
Versandbedingung
dry ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Posttranslationale Modifikation Target
unmodified
Angaben zum Gen
human ... EDEM2(55741)
mouse ... Edem2(108687)
rat ... Edem2(296304)
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Immunogen
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Physikalische Form
Haftungsausschluss
Sie haben nicht das passende Produkt gefunden?
Probieren Sie unser Produkt-Auswahlhilfe. aus.
Lagerklassenschlüssel
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
nwg
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Die passende Version wird nicht angezeigt?
Wenn Sie eine bestimmte Version benötigen, können Sie anhand der Lot- oder Chargennummer nach einem spezifischen Zertifikat suchen.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.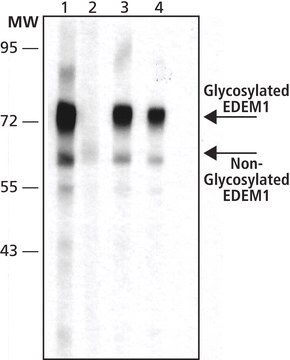
![(±)-(E)-4-Ethyl-2-[(E)-hydroxyimino]-5-nitro-3-hexenamide ≥98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/404/859/0c6eb80d-2c3c-4bf1-98e8-1b319b597b12/640/0c6eb80d-2c3c-4bf1-98e8-1b319b597b12.png)