Wichtige Dokumente
32402
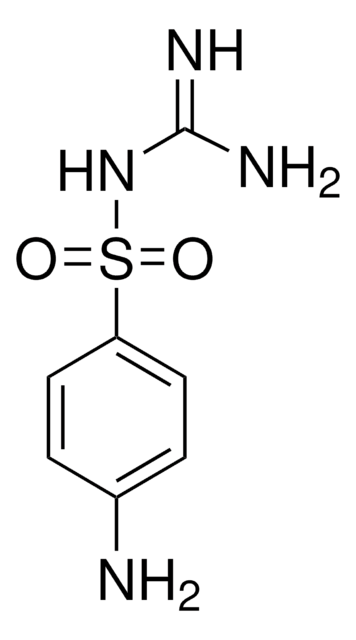
Sulfaguanidin
VETRANAL®, analytical standard
Synonym(e):
4-Amino-N-(aminoiminomethyl)-benzolsulfonamid, 4-Amino-N-guanylbenzolsulfonamid
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
analytical standard
Qualitätsniveau
Produktlinie
VETRANAL®
Haltbarkeit
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
Methode(n)
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
Anwendung(en)
clinical testing
Format
neat
SMILES String
NC(=N)NS(=O)(=O)c1ccc(N)cc1
InChI
1S/C7H10N4O2S/c8-5-1-3-6(4-2-5)14(12,13)11-7(9)10/h1-4H,8H2,(H4,9,10,11)
InChIKey
BRBKOPJOKNSWSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
- Food samples of animal origin by salting-out supported liquid extraction (SOSLE) and quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe (QuEChERS) extraction followed by analysis using nanoflow liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS).
- Bovine muscle samples by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry (HILIC-ESI-MS/MS) equipped with selected reaction monitoring (SRM) mode of detection.
- Tissues, milk and eggs of food producing animals by ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), solid phase extraction (SPE) and LC-MS/MS.
- Beeswax by solid-liquid extraction (SLE), liquid-liquid extraction (LLE), SPE, QuEChERS extraction and ESI-LC-MS/MS with SRM detection.
Rechtliche Hinweise
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Respiratory system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Die passende Version wird nicht angezeigt?
Wenn Sie eine bestimmte Version benötigen, können Sie anhand der Lot- oder Chargennummer nach einem spezifischen Zertifikat suchen.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.