Wichtige Dokumente
07562
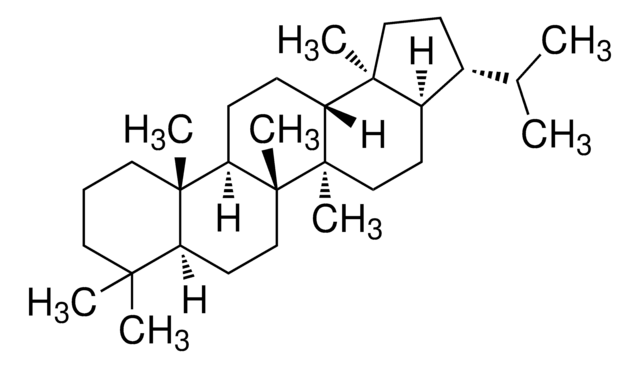
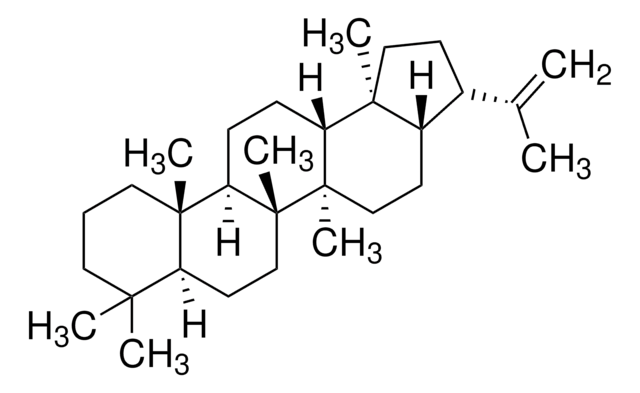
17β(H),21β(H)-Hopan -Lösung
0.1 mg/mL in isooctane, analytical standard
Synonym(e):
A′-Neogammaceran
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
analytical standard
Qualitätsniveau
Haltbarkeit
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
Konzentration
0.1 mg/mL in isooctane
Anwendung(en)
food and beverages
Format
single component solution
Lagertemp.
−20°C
SMILES String
[H][C@@]12CC[C@]3(C)[C@]([H])(CC[C@]4([H])[C@@]5(C)CCCC(C)(C)[C@]5([H])CC[C@@]34C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H]2C(C)C
InChI
1S/C30H52/c1-20(2)21-12-17-27(5)22(21)13-18-29(7)24(27)10-11-25-28(6)16-9-15-26(3,4)23(28)14-19-30(25,29)8/h20-25H,9-19H2,1-8H3/t21-,22+,23+,24-,25-,27+,28+,29-,30-/m1/s1
InChIKey
ZRLNBWWGLOPJIC-PYQRSULMSA-N
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Asp. Tox. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Central nervous system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flammpunkt (°F)
10.4 °F - closed cup
Flammpunkt (°C)
-12 °C - closed cup
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Leider sind derzeit keine COAs für dieses Produkt online verfügbar.
Wenn Sie Hilfe benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an Kundensupport
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.