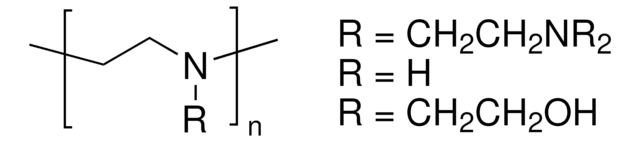Wichtige Dokumente
764582
Polyethylenimin, linear
average Mn 5,000, PDI ≤1.3
Synonym(e):
PEI
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Form
solid
Qualitätsniveau
Mol-Gew.
average Mn 5,000
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
54-59 °C
PDI
≤1.3
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
N1CC1
InChI
1S/C2H5N/c1-2-3-1/h3H,1-2H2
InChIKey
NOWKCMXCCJGMRR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Verwandte Kategorien
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Delivery of Nucleic Acids Using Polymers
Gene therapy has become one of the most discussed techniques in biomedical research in recent years.
Professor Yoshiki Katayama (Kyushu University, Japan) discusses recent advances in drug delivery systems and strategies that exploit the EPR effect, with a special focus on stimuli-responsive systems based on novel materials.
Wide range of functional polymers for biomedical applications have been synthesized and structurally characterized. Several classes of polymers including biodegradable polymers, hydrophilic & amphiphilic polymers, and stimuli responsive polymers have been prepared using controlled and directed functionalization via "living" polymerization such as RAFT, ionic and ring opening polymerization. Selected polymers have been studied for their structure-properties relationship. "
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 764582-1G | 4061832923048 |
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.