Wichtige Dokumente
380210
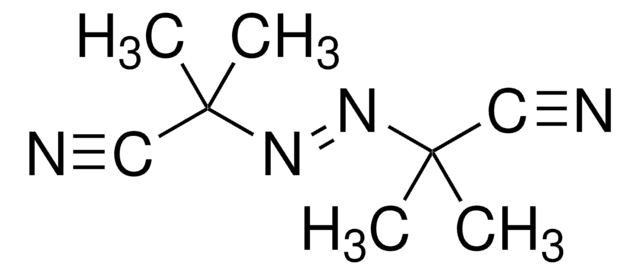
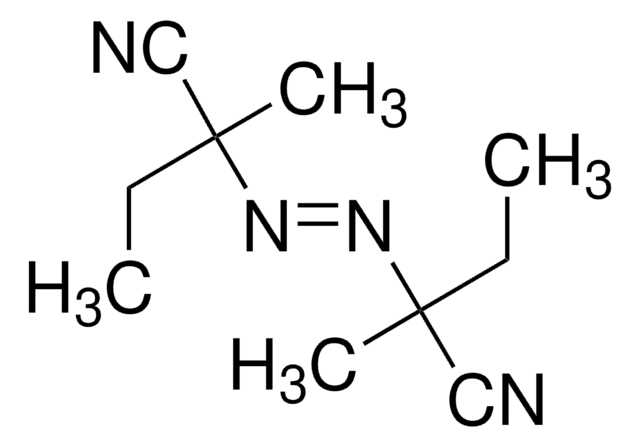
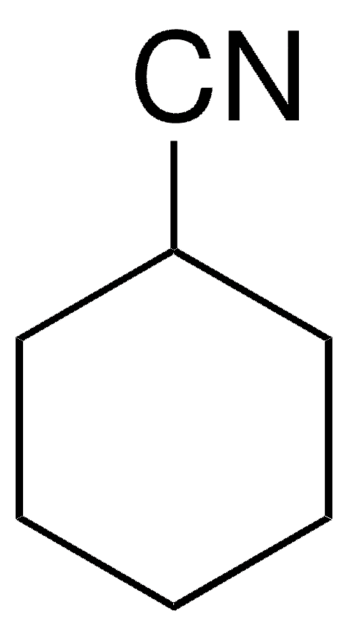
1,1′-Azobis(cyclohexancarbonitril)
98%
Synonym(e):
1,1′-Azobis(cyanocyclohexan), ACHN, VAZO™ Katalysator 88 freie Radikalquelle
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
98%
Form
solid
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
114-118 °C (lit.)
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
N#CC1(CCCCC1)\N=N\C2(CCCCC2)C#N
InChI
1S/C14H20N4/c15-11-13(7-3-1-4-8-13)17-18-14(12-16)9-5-2-6-10-14/h1-10H2/b18-17+
InChIKey
KYIKRXIYLAGAKQ-ISLYRVAYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2 - Self-react. D - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Respiratory system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
5.2 - Organic peroxides and self-reacting hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Tools for Performing ATRP
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Applying ARGET ATRP to the Growth of Polymer Brush Thin Films by Surface-initiated Polymerization
Protokolle
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.