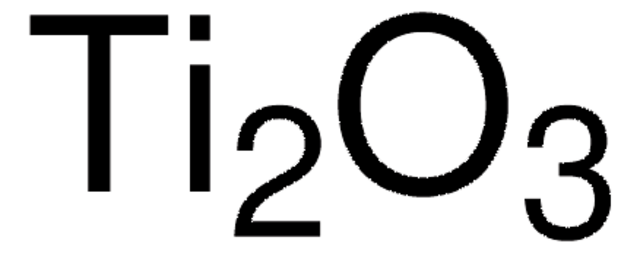Wichtige Dokumente
204730
Titan(IV)-oxid, Rutil
99.995% trace metals basis
Synonym(e):
Titandioxid
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
99.995% trace metals basis
Form
powder and chunks
Eignung der Reaktion
reagent type: catalyst
core: titanium
Dichte
4.17 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES String
O=[Ti]=O
InChI
1S/2O.Ti
InChIKey
GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
- Preparation of Visible Light Photocatalytic Graphene Embedded Rutile Titanium(IV) Oxide Composite Nanowires and Enhanced NOx Removal: This study involves the development of graphene-embedded rutile TiO2 nanocomposites for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of NOx under visible light, which is significant for environmental cleanup technologies (Lee et al., 2019).
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
nwg
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
A Review of Mesoporous TiO2 Thin Films
The prevailing strategies for heat and electric-power production that rely on fossil and fission fuels are having a negative impact on the environment and on our living conditions.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 204730-25G | 4061838767202 |
| 204730-5G | 4061838767219 |
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.