SRP0189
Pyruvate kinase M2 Active from mouse
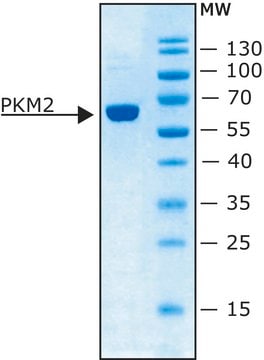
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonyme(s) :
M2-PK tumor, OPA-interacting protein 3 (OIP-3), Pyruvate kinase 3 (PK3), Pyruvate kinase, muscle, Thyroid hormone-binding protein 1 (THBP1)
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
mouse
Produit recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Pureté
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
aqueous solution
Poids mol.
58 kDa
Conditionnement
pkg of 20 μg
Conditions de stockage
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
Concentration
>0.02 mg/mL
Numéro d'accès NCBI
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Conditions d'expédition
dry ice
Température de stockage
−70°C
Informations sur le gène
mouse ... PKM2(18746)
Description générale
Murine Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) (GenBank Accession No. NM_011099), amino acids 2-end, with N-terminal His tag, MW = 58kDa, expressed in an Escherichia coli expression system.
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Définition de l'unité
Forme physique
Notes préparatoires
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Articles
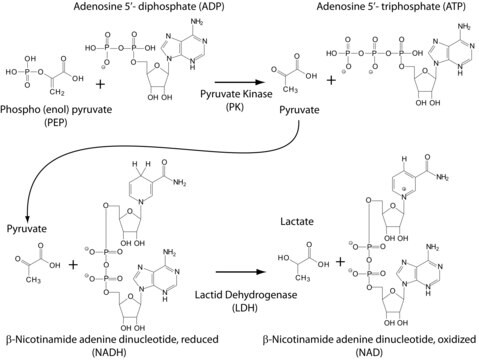
We presents an article about the Warburg effect, and how it is the enhanced conversion of glucose to lactate observed in tumor cells, even in the presence of normal levels of oxygen. Otto Heinrich Warburg demonstrated in 1924 that cancer cells show an increased dependence on glycolysis to meet their energy needs, regardless of whether they were well-oxygenated or not.
We presents an article about the Warburg effect, and how it is the enhanced conversion of glucose to lactate observed in tumor cells, even in the presence of normal levels of oxygen. Otto Heinrich Warburg demonstrated in 1924 that cancer cells show an increased dependence on glycolysis to meet their energy needs, regardless of whether they were well-oxygenated or not.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique